Chinese landscape painting (which had already formed a separate painting discipline and academic theoretical system during the Southern and Northern Dynasties period from 220 to 589) is actually a depiction of scenery. The term 'Landscape' was introduced to China between 1576-1610 with the use of Western art forms such as oil painting.
Murals depicting landscapes were discovered in Pompeii, Naples province, Campania region, Italy (Pompeii became a territory of the Roman Empire in 82 BC and was buried in 79 AD due to the eruption of Mount Vesuvius).

Pompeii Ancient City Murals
In the 14th century, Ambrogio Lorenzetti (Italy, 1290-1348), a painter of the "Siena School" influenced by the "Florentine School", created murals such as "The Influence of Good Rural Government" and "The Influence of Bad Rural Government" at the Siena City Hall in the Siena Province of Tuscany, Italy, which included depictions of scenery.
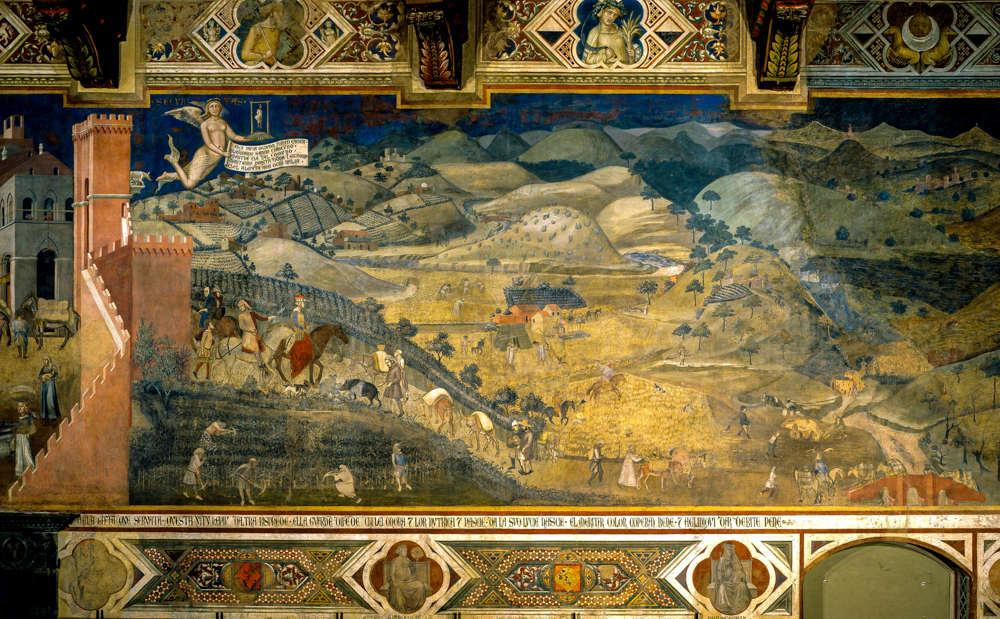

Ambrogio Lorenzetti's' The Influence of Good Rural Government '
In the 15th century, Hubert Van Eyck (Netherlands, 1370-1426), known as the "father of oil painting", Jan Van Eyck (Netherlands, 1395-1441), Rogier van der Weyden (Netherlands, 1399-1464), and Hans Memling (Germany, 1430-1494), who mainly engaged in religious and portrait painting, created a large proportion of landscapes in some of the paintings of the "Netherland School" (which included some regions such as present-day Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and France).
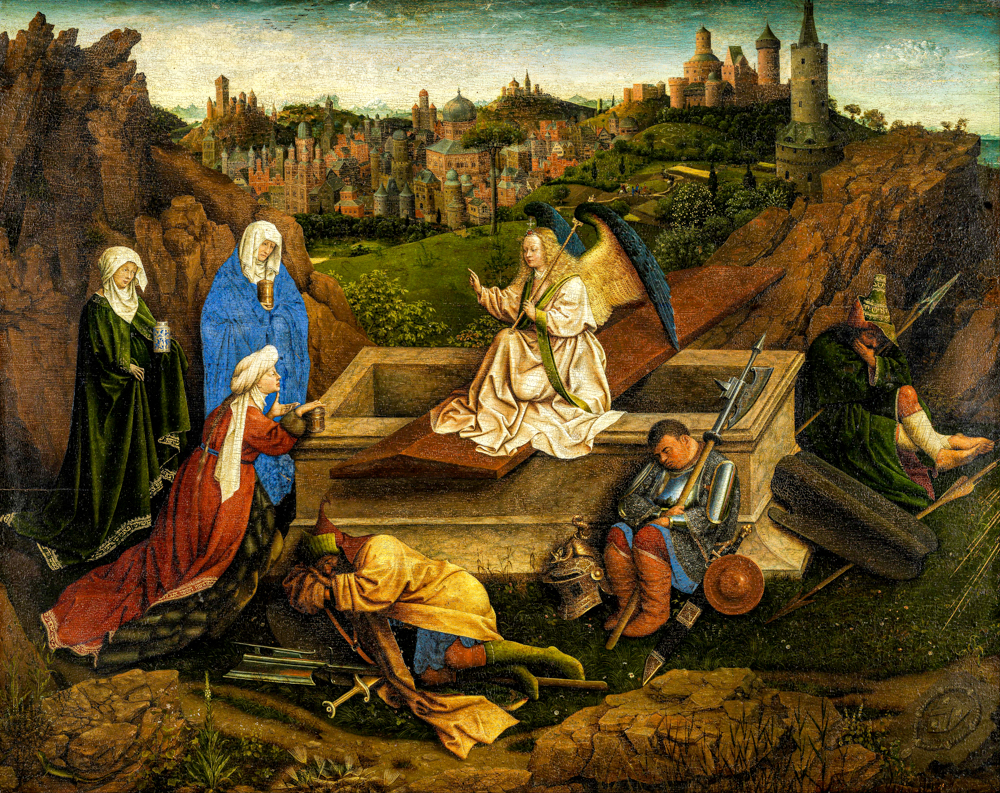

Hubert van Eyck's "The Three Saints at the Empty Tomb"

Jan van Eyck's "Praise of the Lamb"
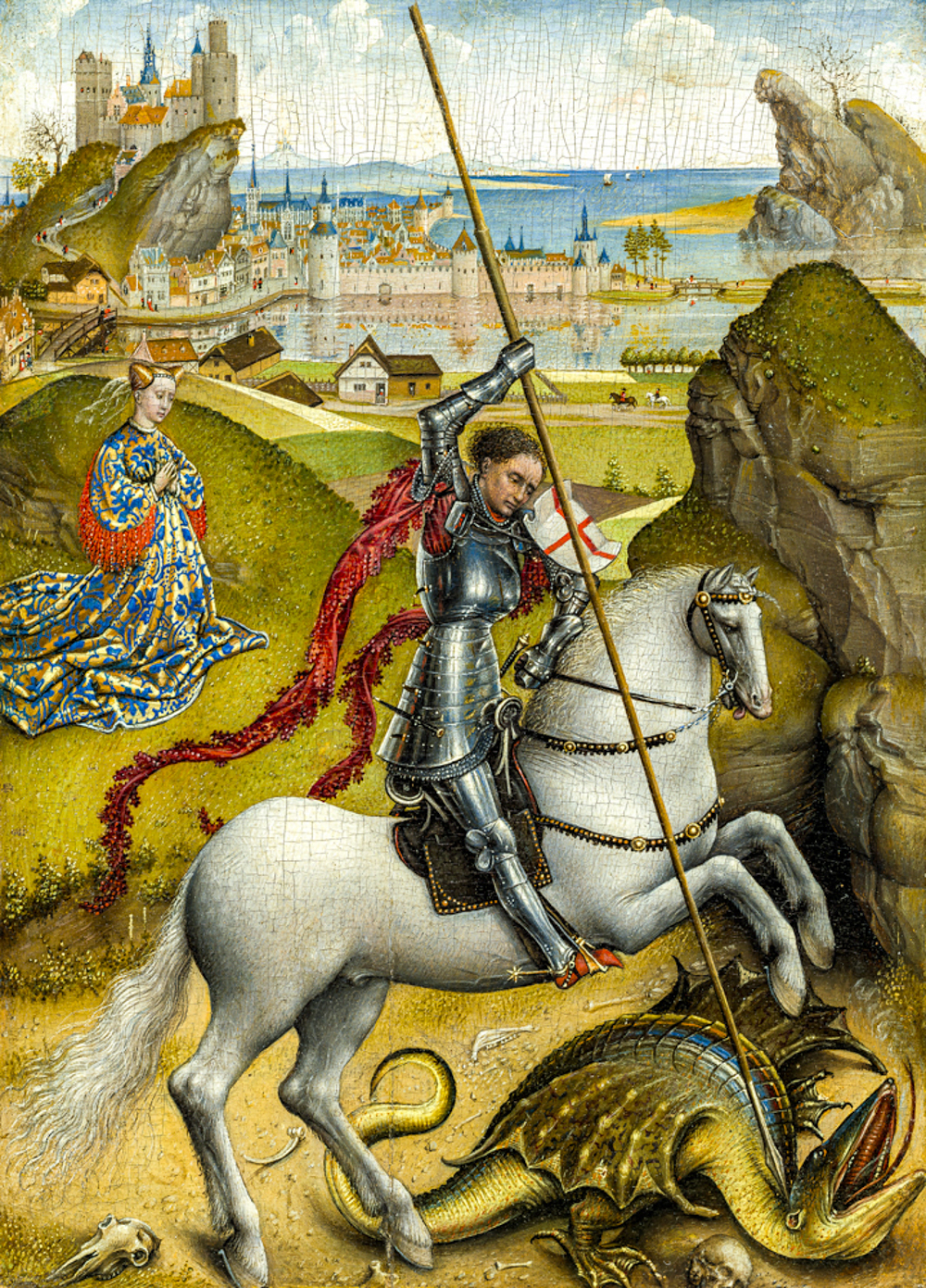

Roger van der Weyden's "St. George and the Dragon"
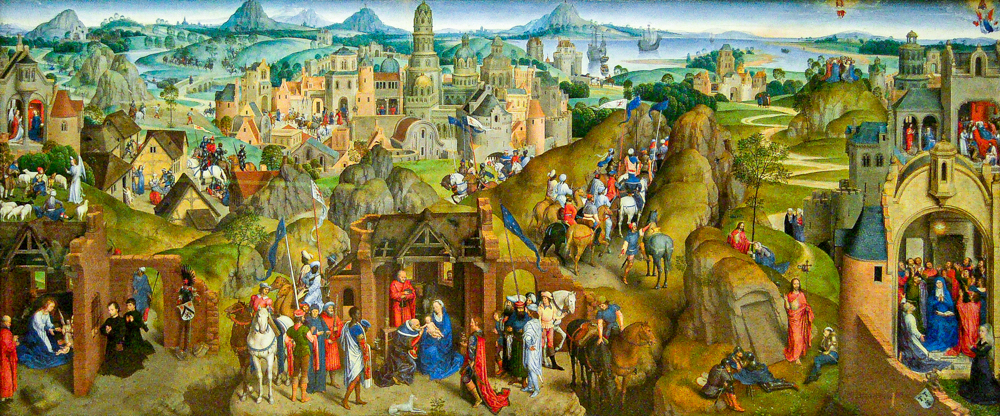

Hans Memlin's "The Coming and Victory of Christ"
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (Italy, 1452-1519), known as one of the "Three Masters of the Renaissance" along with Michelangelo Bonaroti and Raphael Sansi in the Roman School, created the first landscape based sketch.
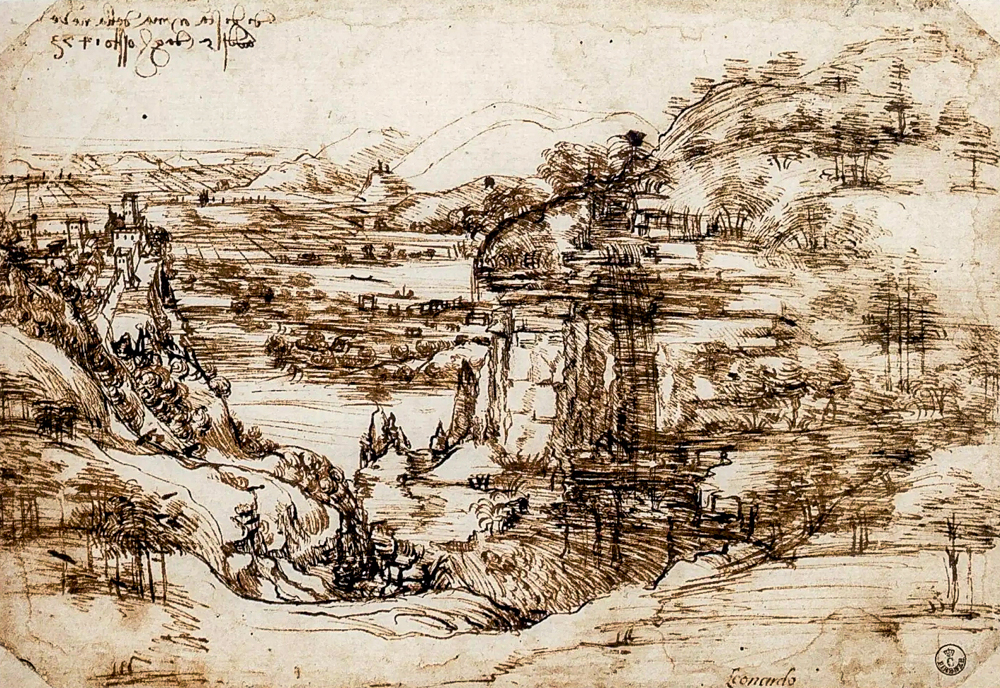

Leonardo da Vinci's "Scenery of the Arno Valley"
In the 16th century, the earliest landscape painter in Europe, Joachim Patenier (Netherlands, 1480-1524), appeared in the "Dutch School of Painting". He often used the technique of "reverse composition" to overlook open panoramas from a high perspective, combining open landscapes with reduced characters, and using reduced characters to express stories and themes. The school of painting also saw the emergence of the earliest European peasant painter, Pieter Bruegel de the Elder (Netherlands, 1525-1569), who valued the observation and study of life. He often went to the countryside with friends to participate in the labor of farmers and depicted more realistic scenes, earning him the nickname "Peasant Bruegel". The Baroque style of Peter Paul Rubens (Belgium, 1577-1640) broke the seriousness, subtlety, and balance of the Renaissance period, advocating luxury and grandeur, and often using curves, arcs, or surfaces to express and emphasize spatial, three-dimensional, and fluid sensations. He and Jan Brueghel the Elder (Netherlands, 1568-1625), the second son of Peter Brueghel the Elder, still carry the style of this school of painting.

Joachim Patiniel's' Scenery of Saint Jerome '
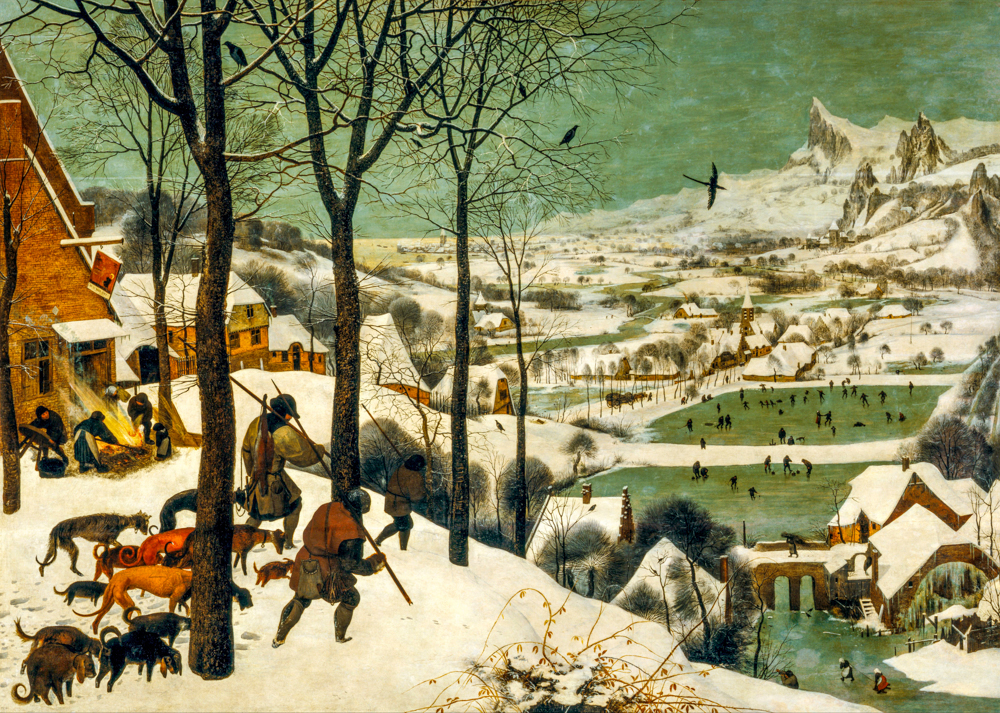

Peter Bruegel's' The Snow Hunter '
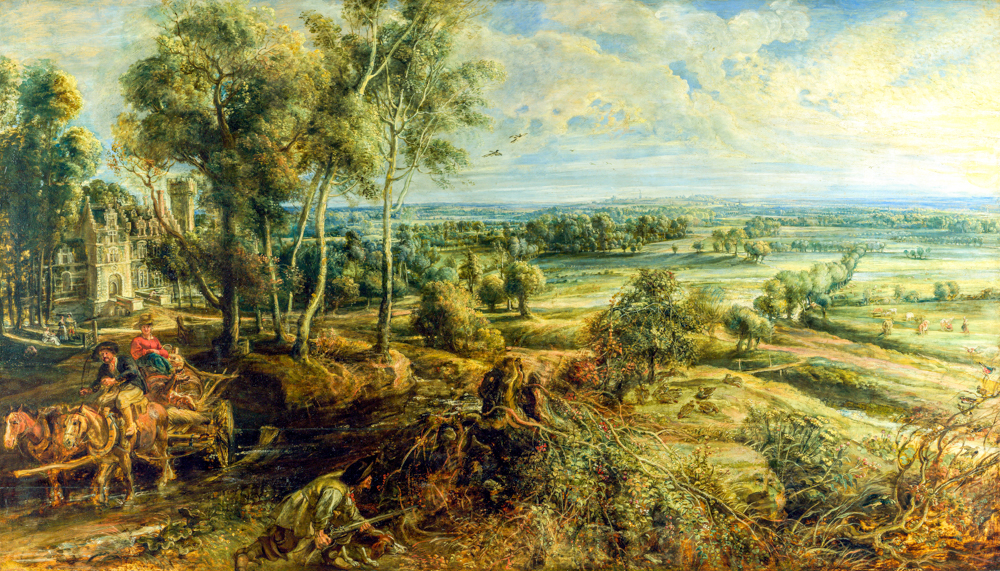

Peter Paul Rubens' 'The Morning of Haitsten'
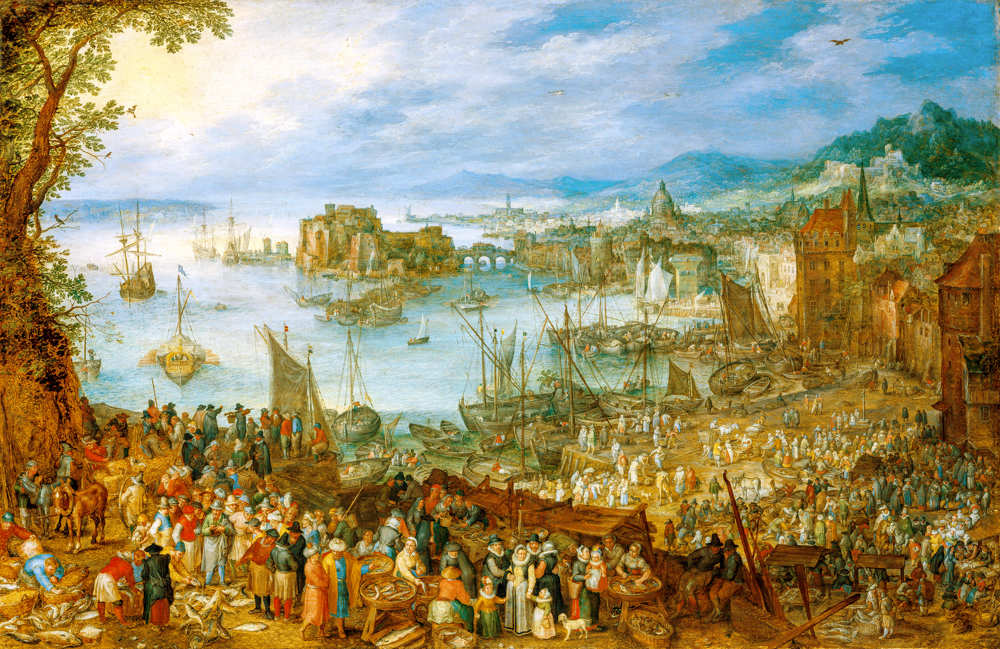

Old Yang Bruegel's' Big Fish Market '
Giorgio O Zorzi Da Castelfranco (Italy, 1477-1510) of the "Venetian School" depicted magnificent colors, vivid forms, and was adept at combining poetic natural landscapes with character images to create a magnificent and beautiful artistic effect. Tiziano Vecelli (Italy, 1488-1576) initially had a delicate style, expressing objects through color and contour, and later developed to primarily rely on light and color to depict objects. His mid period style influenced Baroque painting, while his later style influenced Romanticism and Impressionism. Giovanni Bellini (Italy, 1430-1516) learned about the use of "oily media" from the paintings of the "Netherland School" and replaced it with the egg tempera method, allowing for deeper and darker colors to be presented in the painting. This provided more room for expression in depicting the interactions between light, air, and matter. The paintings of Paolo Veronese (Italy, 1528-1588) feature vibrant colors and unique perspectives, depicting stylized landscapes used for palace decoration and influencing Baroque painting. Tintoretto/Jacopo Robusti (Italy, 1518-1594) inherited the style of Titian Vercellio while also innovating in his works. In terms of narrative and emotional transmission, he imitated Michelangelo Bonaroti, highlighting strong movements and rich, dreamlike colors. Jacopo dal Ponte (Italy, 1510-1592) depicted farmers, animals, and still life in a realistic and vivid manner, showing a tendency towards realism and creating a photochromic painting style that depicted the ultimate in light and atmosphere.

Joel Joe Barbarelli da Castellano's "The Tempest"
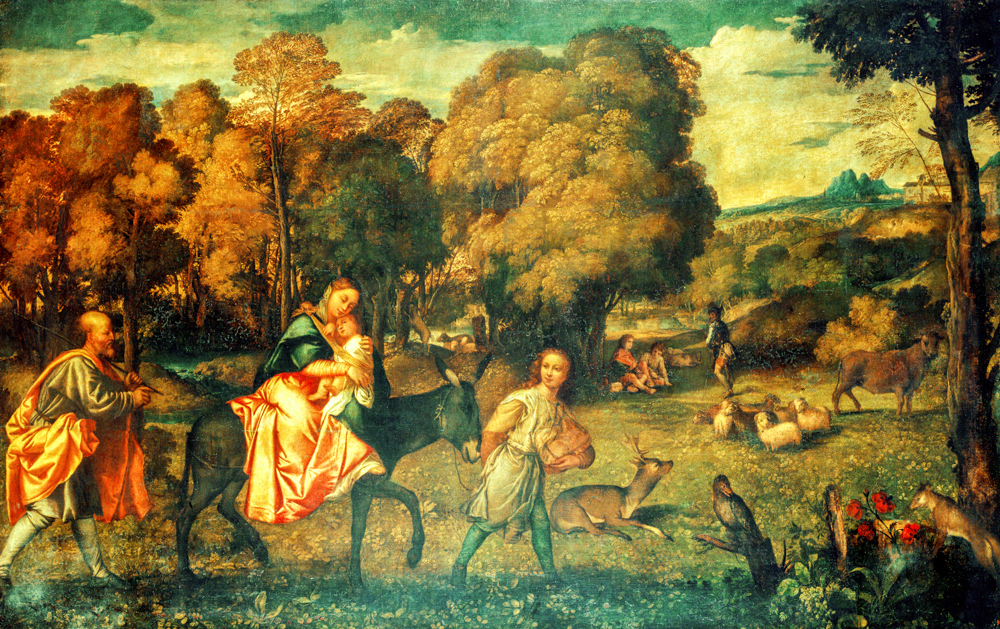

Titian Vercellio's "Escape to Egypt"
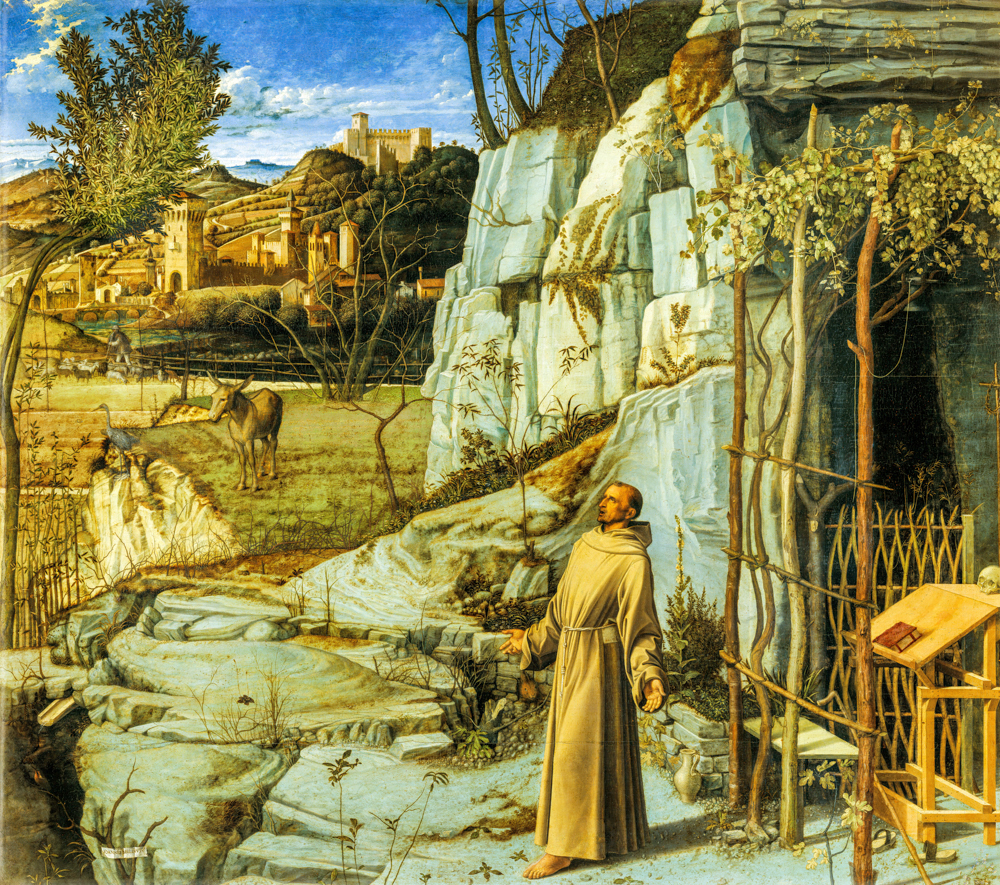

Giovanni Bellini's' St. Francis in the Desert '
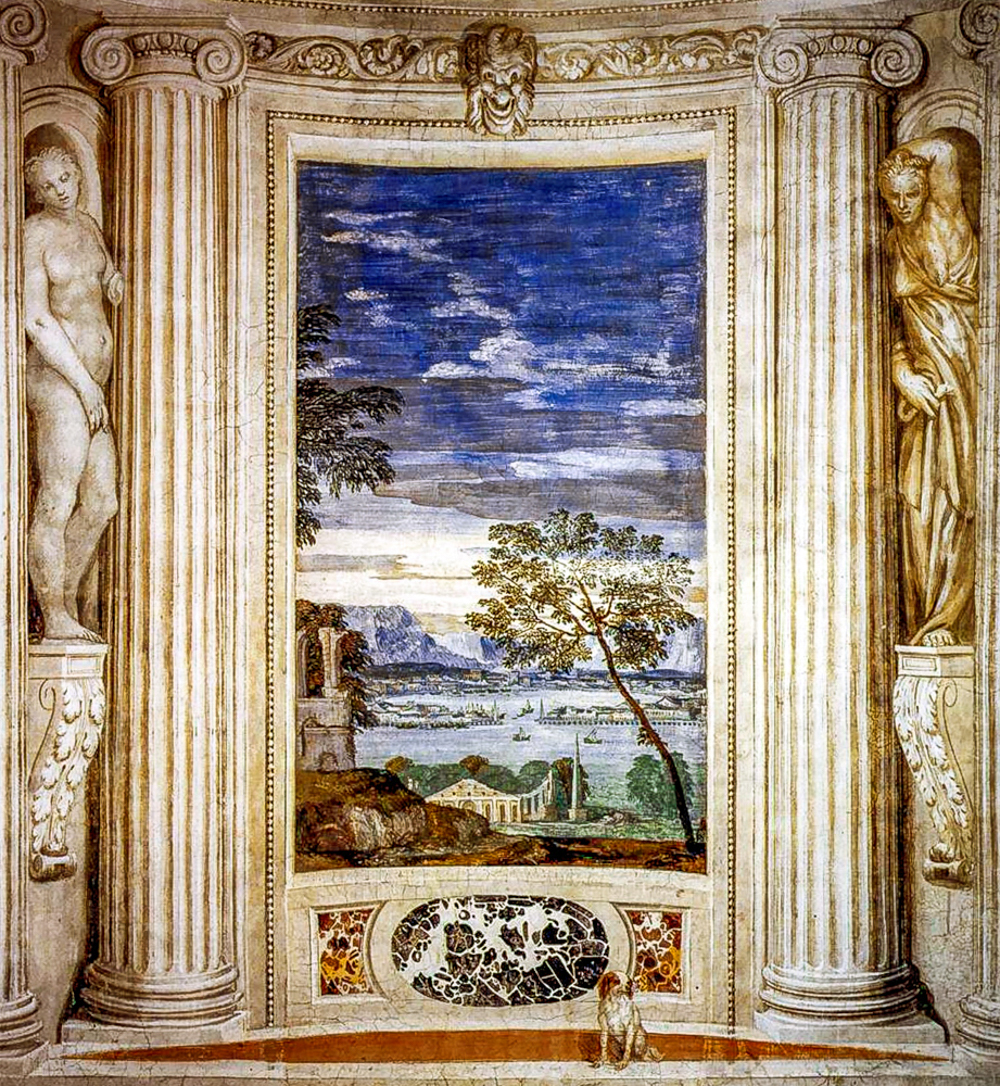

Paul Veronese's' Harbor Scenery '
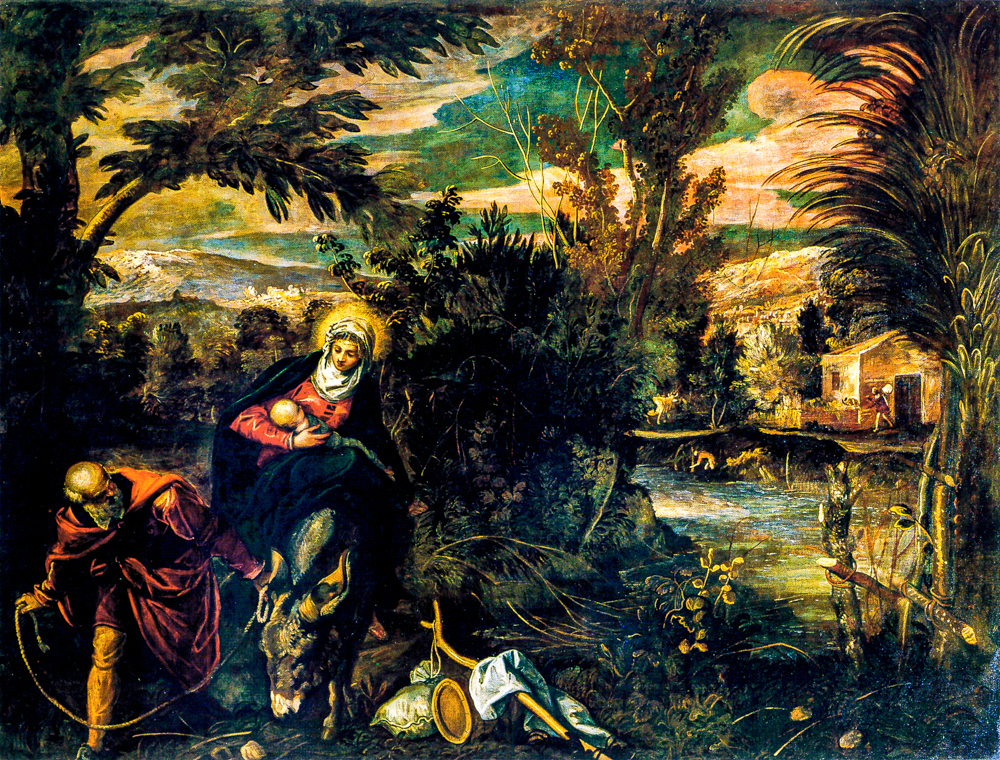

Tintoretto/Jacob Robusti's "Escape to Egypt"
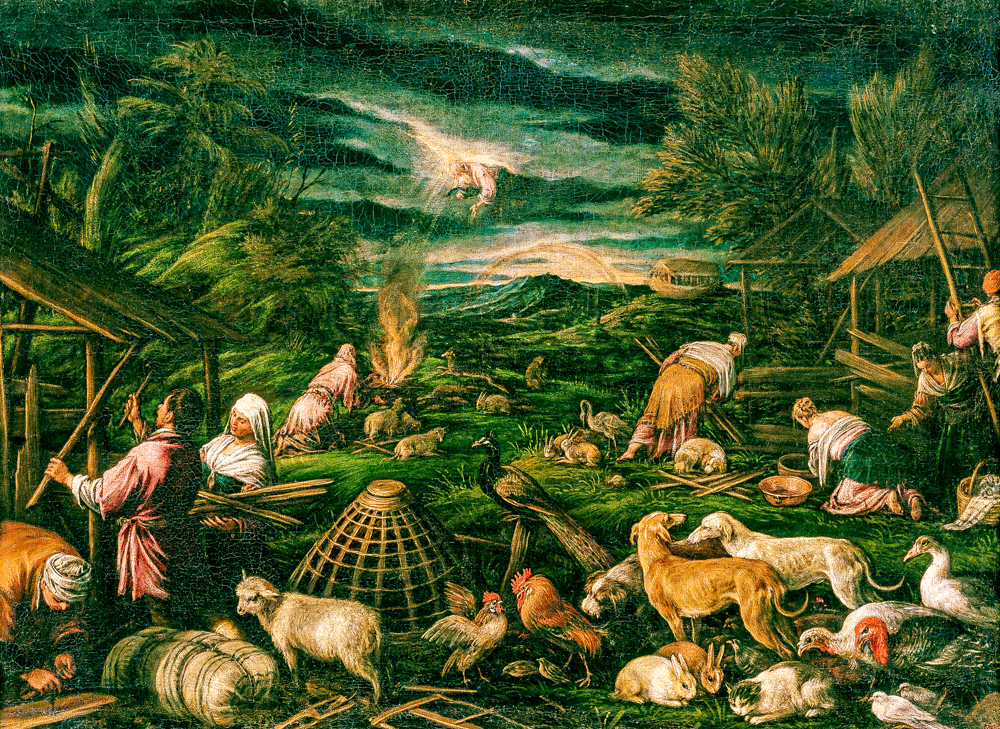

Jacob Bassano's' Noah after the Flood '
Albrecht D ü rer (Germany, 1471-1528), the earliest painter in Europe to create watercolor sketches of natural landscapes, spread the forms and theories of the Italian Renaissance to northern Europe, laying the foundation for the "German National Painting School". The German painting tradition preserved the Gothic style in his works, and his later works were the first to showcase Baroque features.
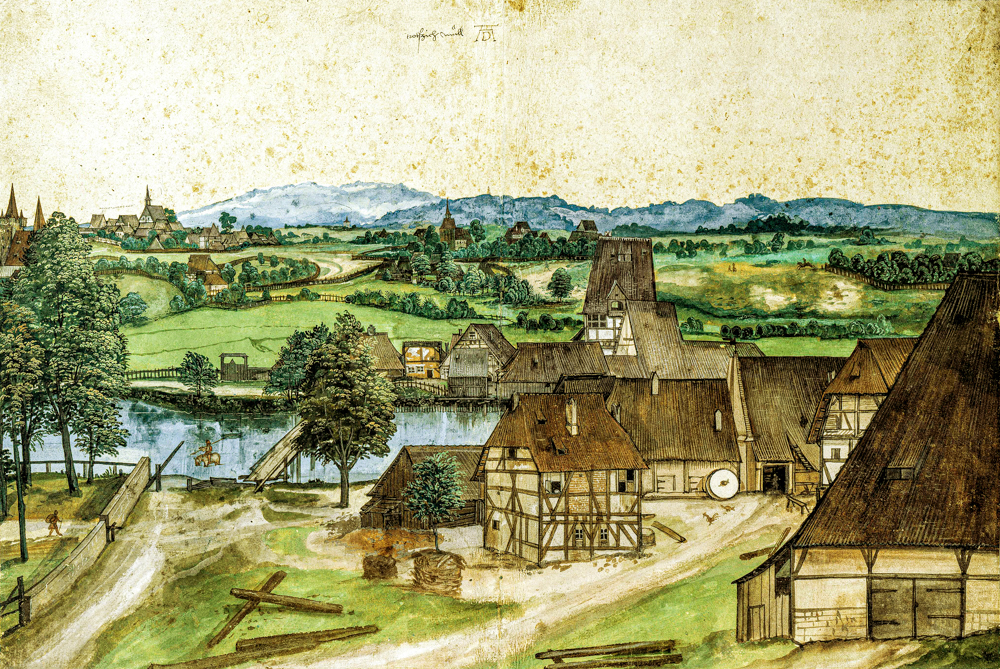

Albrecht D ü rer's "Drawing Works near Nuremberg"
The painters of the Danube School, which was the earliest in Europe to depict forests, sunsets, and ruins, broke the rigorous classical creation style of Italy and became the earliest realistic painting school in the West to sketch landscapes. Albrecht Altdorfer (Germany, 1480-1538) inherited and broke through the landscape that was only used as a background in Albrecht D ü rer's paintings. His painting "Danube Landscape and Walter Castle" became the first pure landscape painting depicting nature, making landscape painting an independent genre. The painters of the Italian "Venetian School" and the "Danube School", such as Lucas Cranach der Aeltere (Germany, 1475-1553), are known as the "earliest explorers of modern European landscape oil painting creation". They truthfully depicted real scenes in a naturalistic way in their paintings.
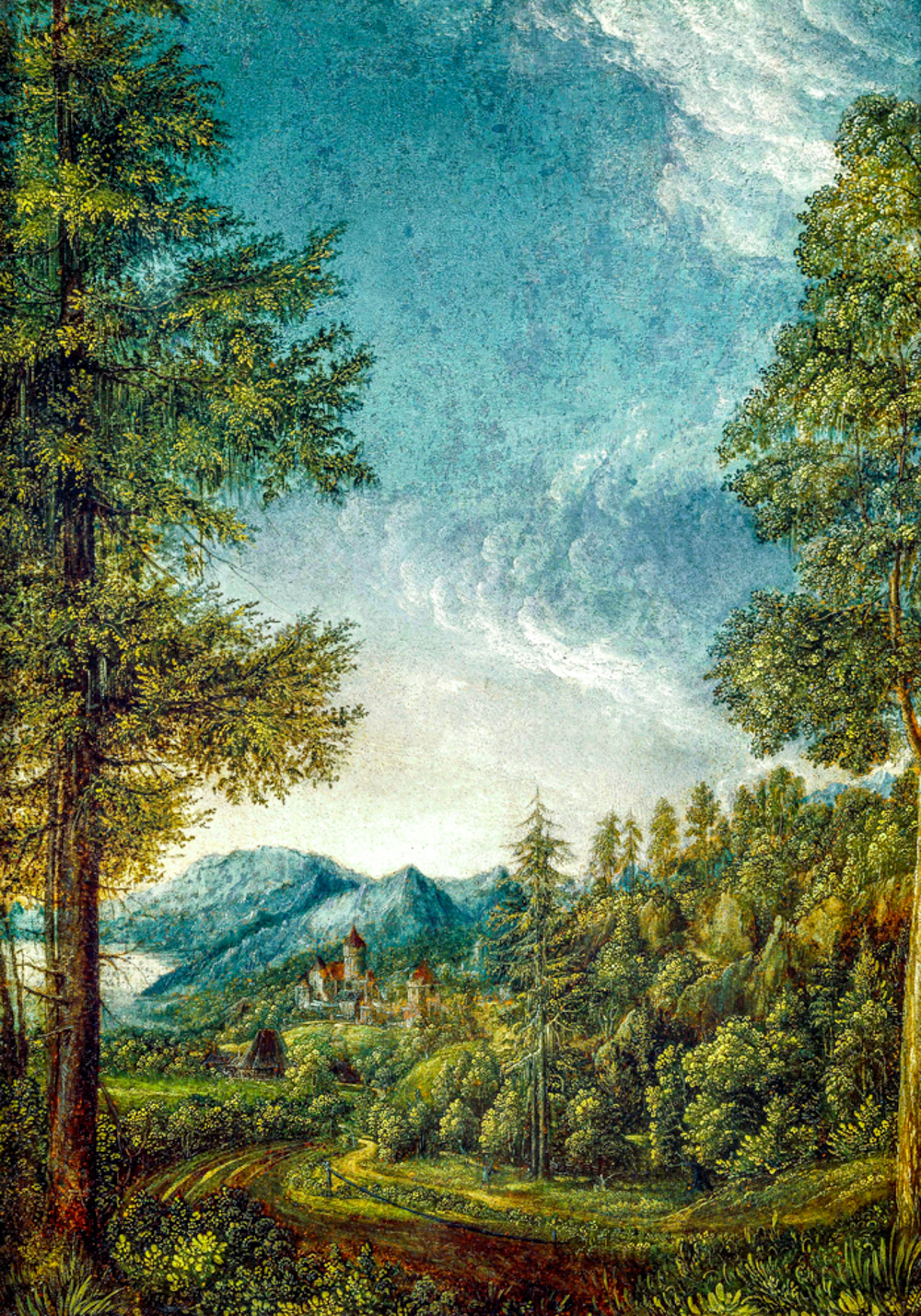

Albrecht Altdofer's "Danube Landscape and Walter Castle"
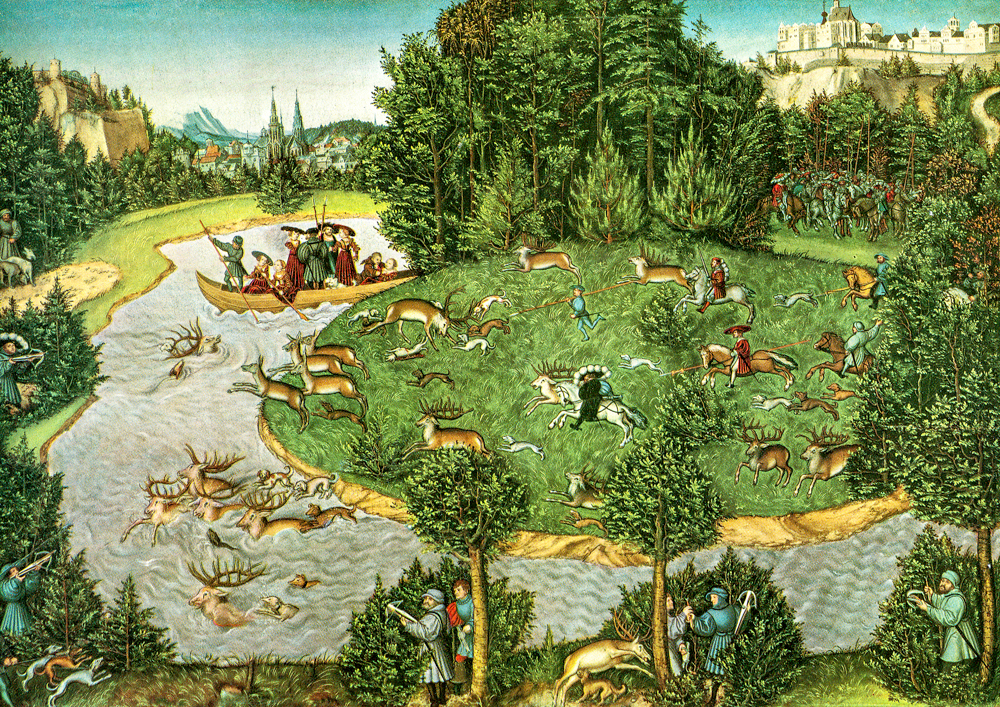

Lucas Cranach's "Hunting Bucks with Elector Wise Friedrich"
Annibale Carracchi (Italy, 1560-1609) presented pastoral landscapes in his paintings, gradually developing the "ideal landscape painting". His landscape paintings had an influence on the creation of Nicolas Pusan and Claude Lorraine, and he was the first person in classical landscape painting (using architecture, street scenes, and natural scenery to express the artistic temperament of "elegance" and "nobility"). Nicolas Poussin (France, 1594-1665), who emphasized poetic expression, and Claude Lorrain (France, 1600-1682), who was skilled in depicting ancient architectural relics, used Roman ruins and suburban rural scenery as their themes, embellishing ancient mythological figures, and were known as "heroic landscape paintings".
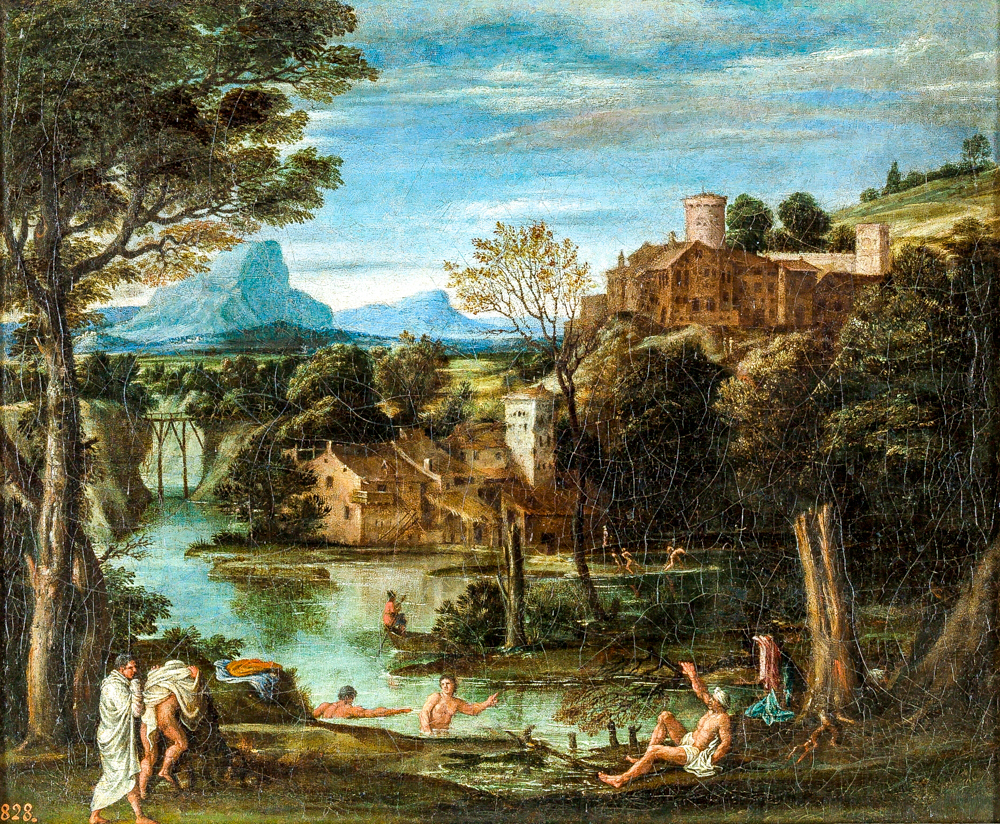

Anibal Karachi's "Scenery, Rivers, and Swimmers"
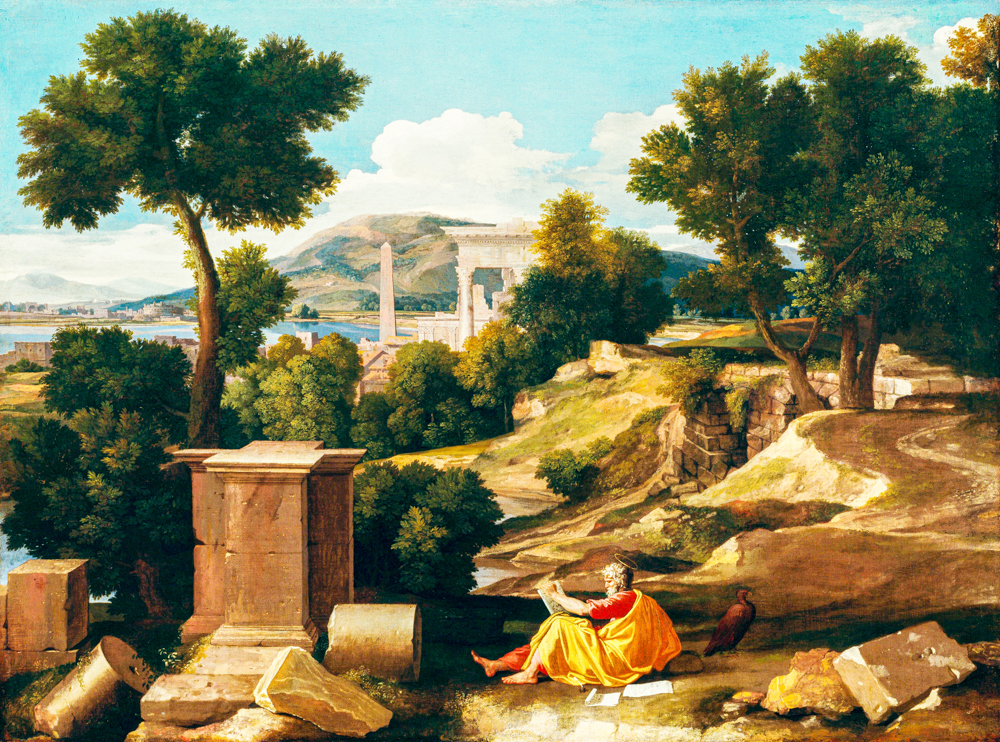

Nicholas Pusan's "Scenery of St. John on the Island of Patmos"
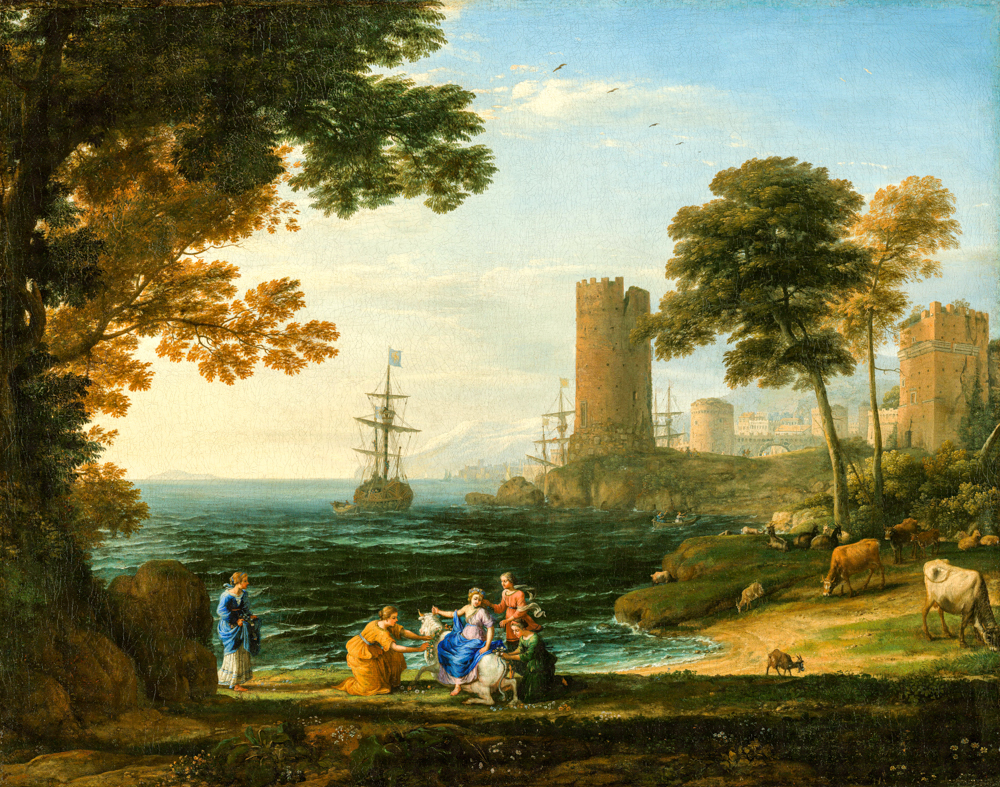

Claude Lorraine's' The Robbed Coast of Europa '
In the 17th century, painters gathered in the picturesque Netherlands to objectively depict the scenery of the region. As the number of works increased, the art trading market also emerged. Aelbert Jacobsz Cuyp (Netherlands, 1620-1691), who studied under his father Jacob Gerritsz Cuyp (1594-1652), was skilled at painting river and ocean landscapes, embellishing them with darker colored figures and livestock, creating a strong contrast with the overall sunny golden environment, depicting the beautiful artistic conception of figures and buildings appearing and disappearing in mist and dawn under the sunshine and sky. Jan Josephszoon van Goyen (Netherlands, 1596-1656), who mainly created works on rivers, was skilled in single tone painting. He was able to handle the color relationship between silver gray water surfaces and yellow brown land well, and often embellished people's daily activities by the river. Jacob van Ruisdael (Netherlands, 1628-1682), who studied under his father Isaack van Ruisdael (1599-1677), was a pioneer of Romanticism, Realism, and Symbolism. He was skilled at depicting the coastline, forests, and strongly contrasting sand dunes of Harlem. In his middle age, his style was majestic and passionate, full of heroic epic tragedy. He used his brush to give the turbulent rivers, cascading waterfalls, castles in the mountains, and desolate ruins a unique charm and artistic conception. Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn (Netherlands, 1606-1669) used the technique of "light and dark" in his oil paintings, which focused light on the main parts of the painting against a dark brown or light brown background, and used precise triangular lighting to outline the contours of the characters, hiding the rest in the light and dark, giving a stable and solemn feeling. Willem van de Velde the Younger (Netherlands, 1633-1707), who studied under his father Willem van de Velde the Elder (Netherlands, 1611-1693), was skilled at depicting beach scenes and coastal ships, paying attention to the movement of light and clouds on the water surface under calm or stormy conditions. With more requests from the government to record the naval battles between the Netherlands and England, his increasingly detailed depictions of ships and the ocean made him a more influential marine painter.Pieter de Hooch (Netherlands, 1629-1684) is famous for his ability to depict the lives of women and children. His paintings abandon the fixed poetic meaning and add more simplicity to daily life. His later works often draw inspiration from the wealthy class of citizens, resulting in magnificent imagery and a return to simplicity in technique and content. The works of Johannes Vermeer (Netherlands, 1632-1675) are like elegant pastoral ballads, showcasing the tranquility and beauty of the Dutch countryside in front of people. The sunshine is bright, the trees are shaded, and the spinning water wheels give the still images a pulsating life. Meindert Hobbema (Netherlands, 1638-1709) focused on direct observation and depiction of nature, often using trees as the main subject and repeatedly depicting similar scenery, using precise painting language to depict realistic objective environments.
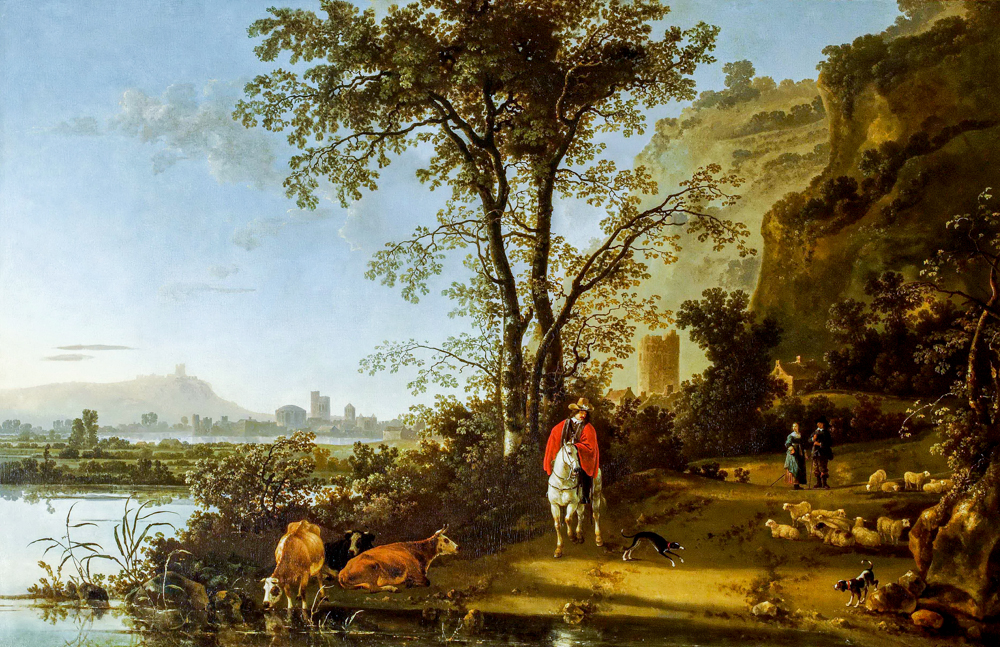

Albert Jacobs Kuiper's "Scenery and Knights, Characters and Cows"
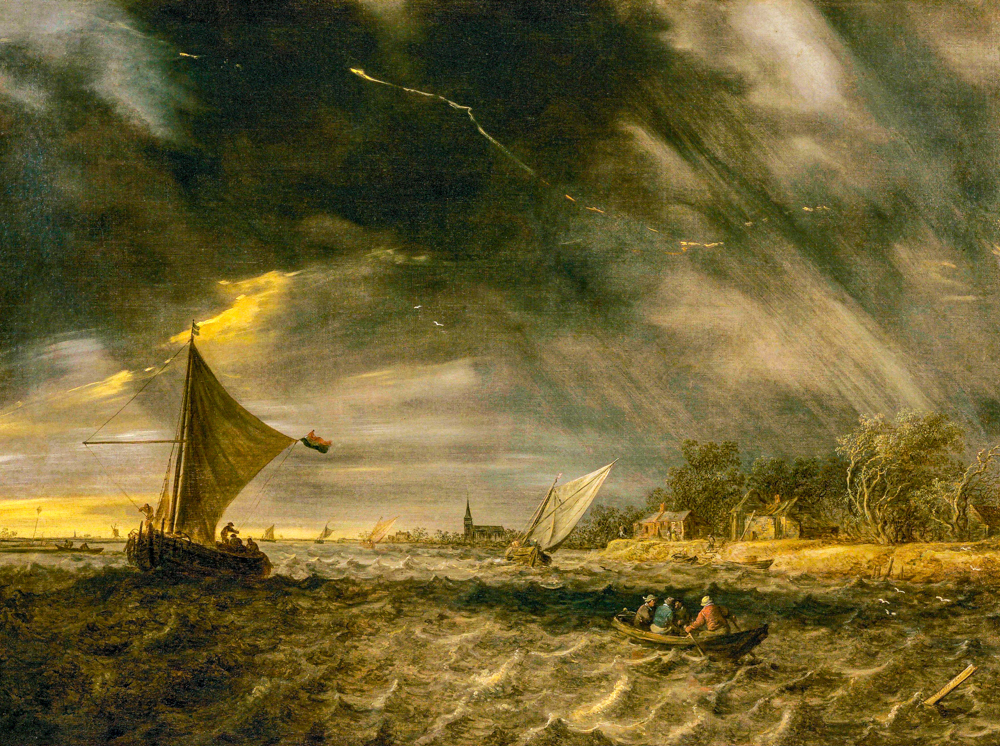

Jan van Hoyan's Thunderstorm
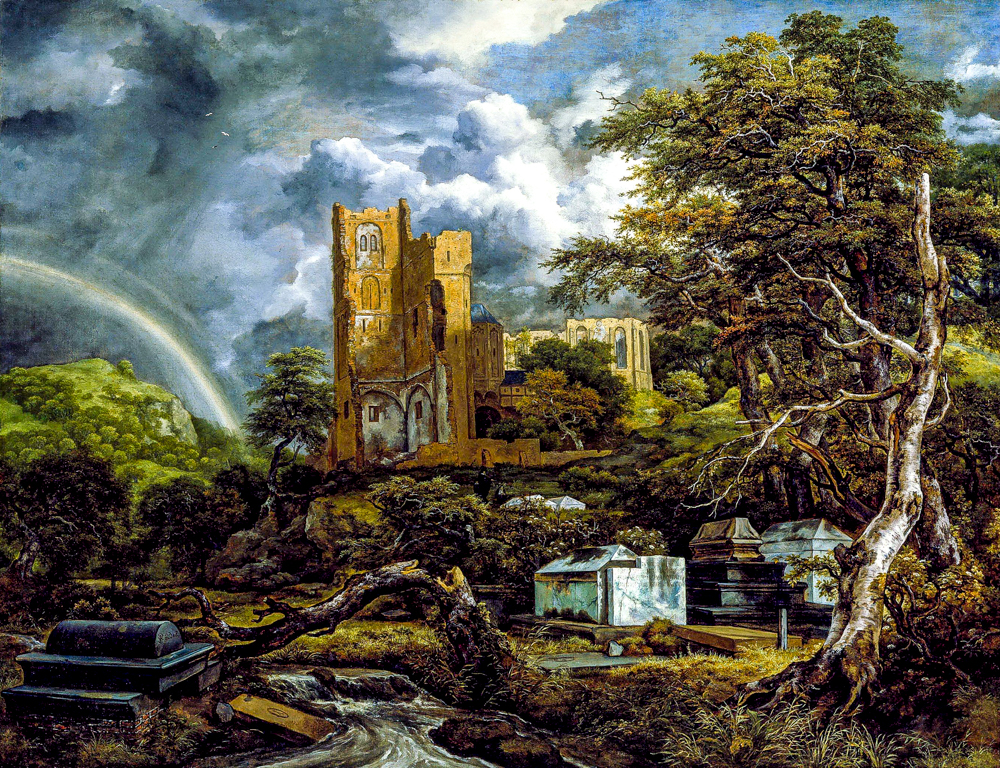

Jacob van Lesdal's "Cemetery"
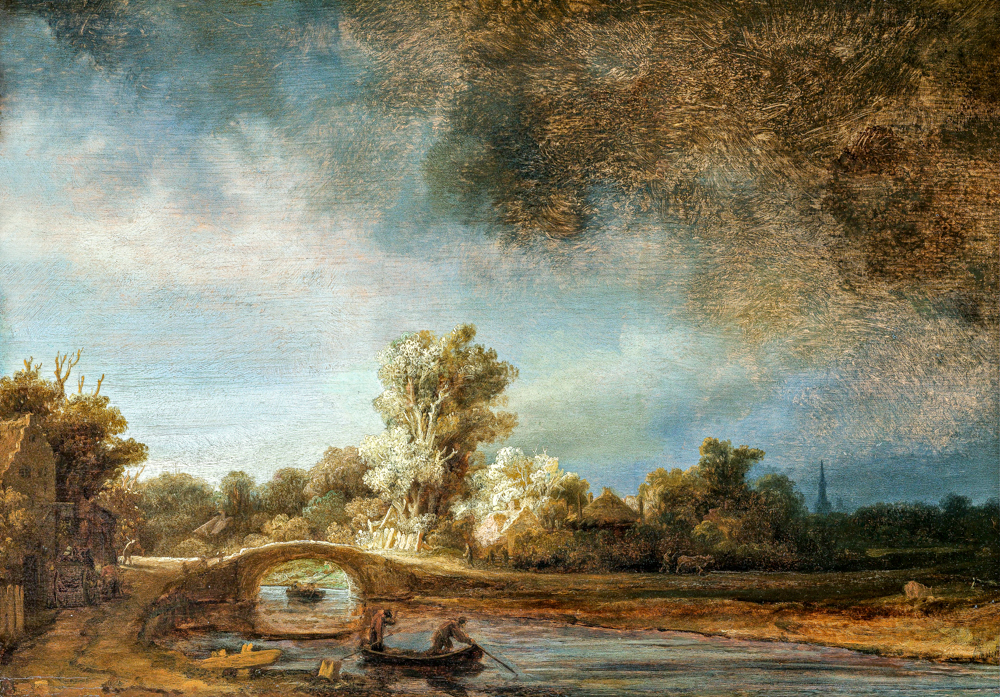
Rembrandt Halmanson van Leyen's "The Stone Bridge"
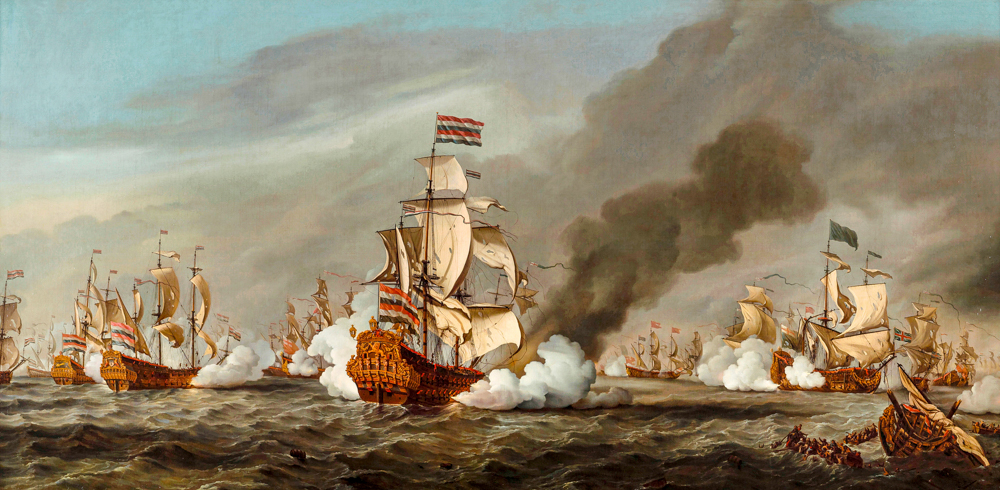

William van der Veld Jr.'s "The Battle of Texel"
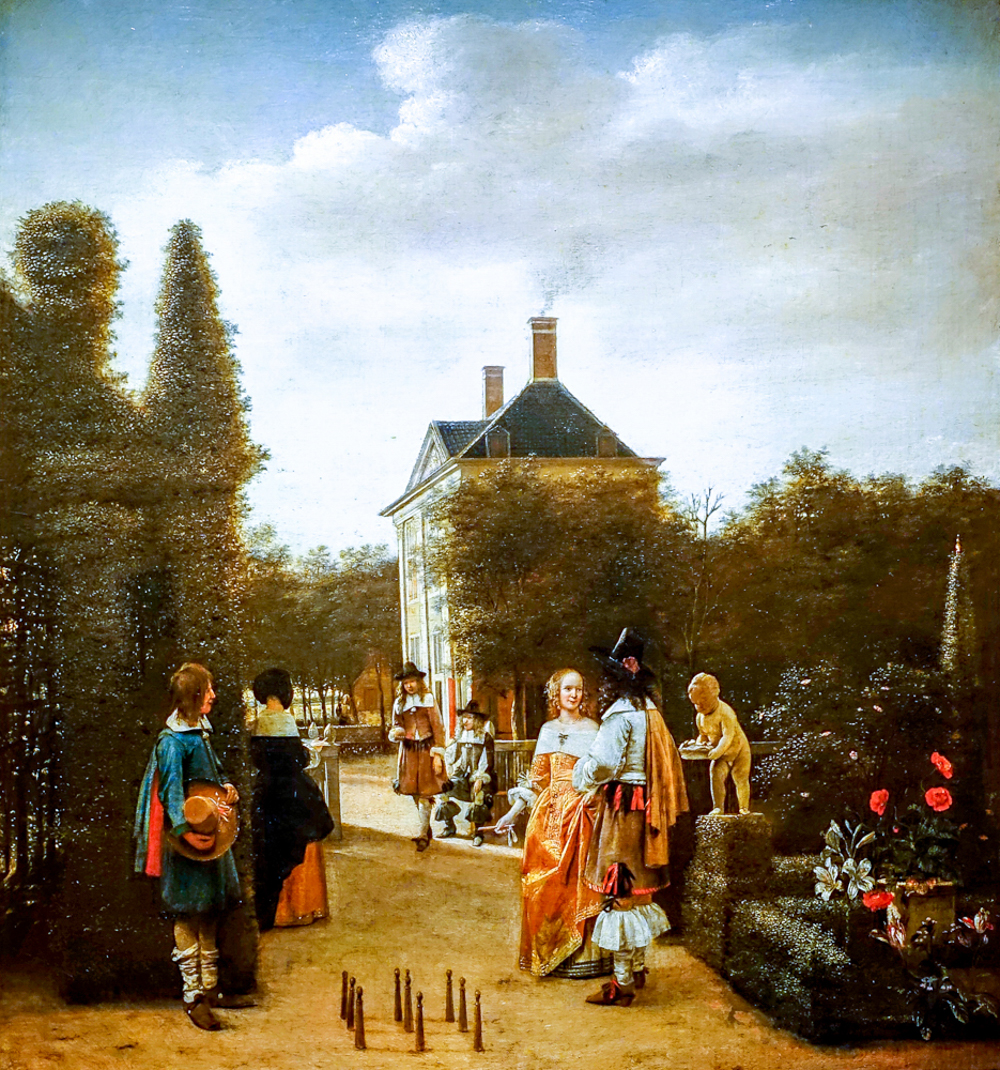
Peter de Hooper's "The Nine Pillars Player in the Garden"

Johannes Vermeer's' Delft Landscape '
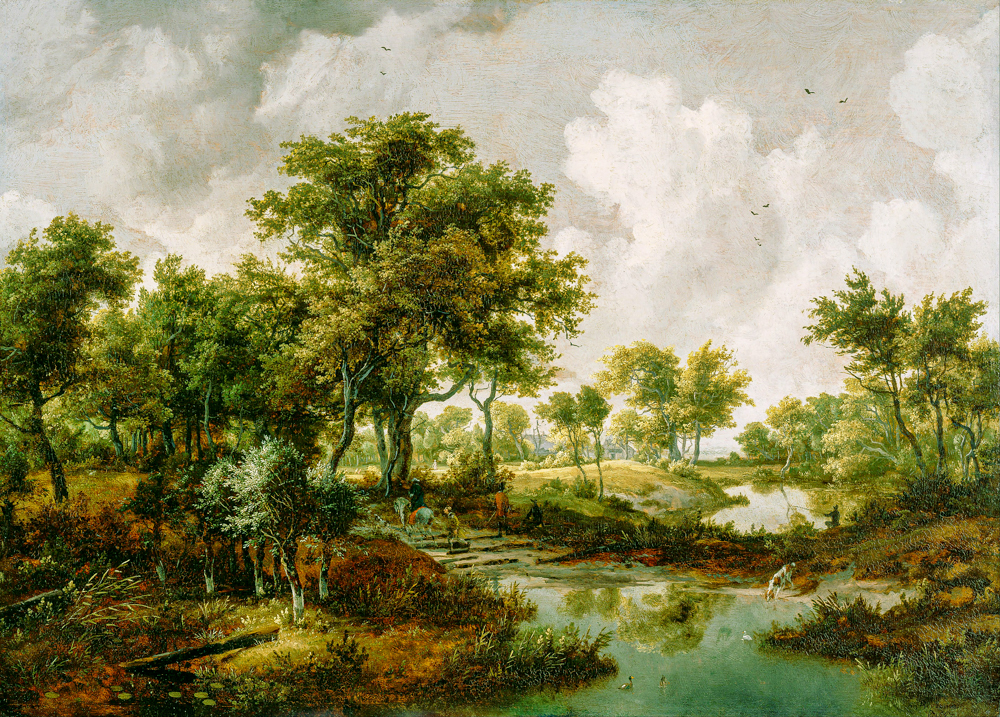

Maindelt Hobema's' Landscape of lush trees'
In the 18th century, Venice became a tourist destination, and "urban landscape paintings" emerged as an accessory. Giovanni Antonio Canale (Italy, 1697-1768) was skilled at painting large-scale urban architectural landscapes. Bernardo Bellotto (Italy, 1721-1780) used a darkbox to draw outlines in some of his paintings, creating an accurate and distortion free sense of scene. Francesco Guardi (Italy, 1712-1793) extensively replicated landscape paintings through etching copperplate prints.
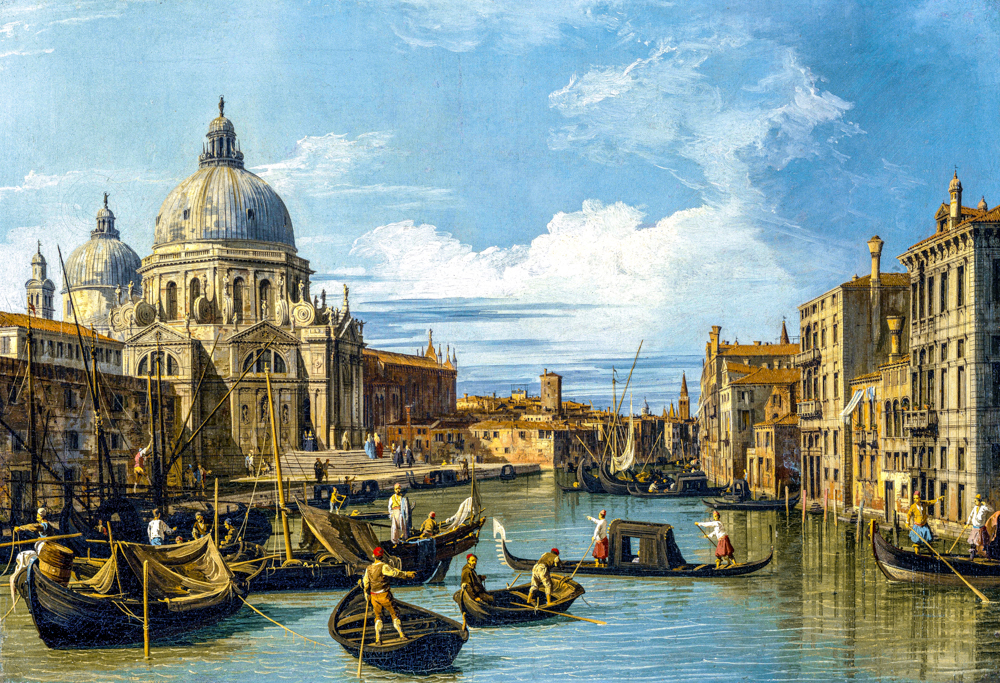

Giovanni Antonio Canaletto's' Entrance to the Grand Canal of Venice '
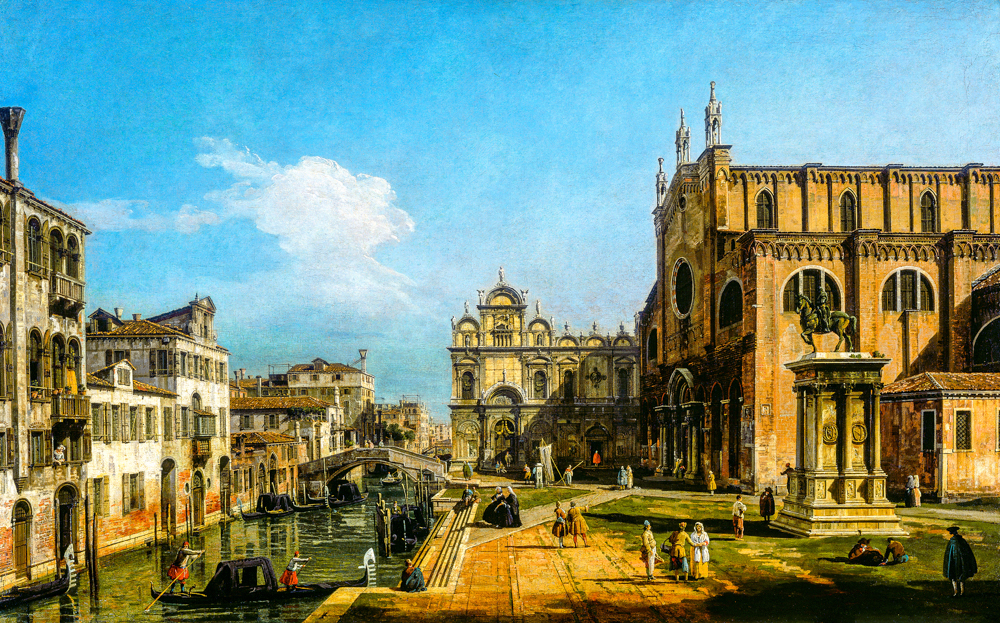

Bernardo Belotto's "San Giovanni and Paul and the School of San Marco"
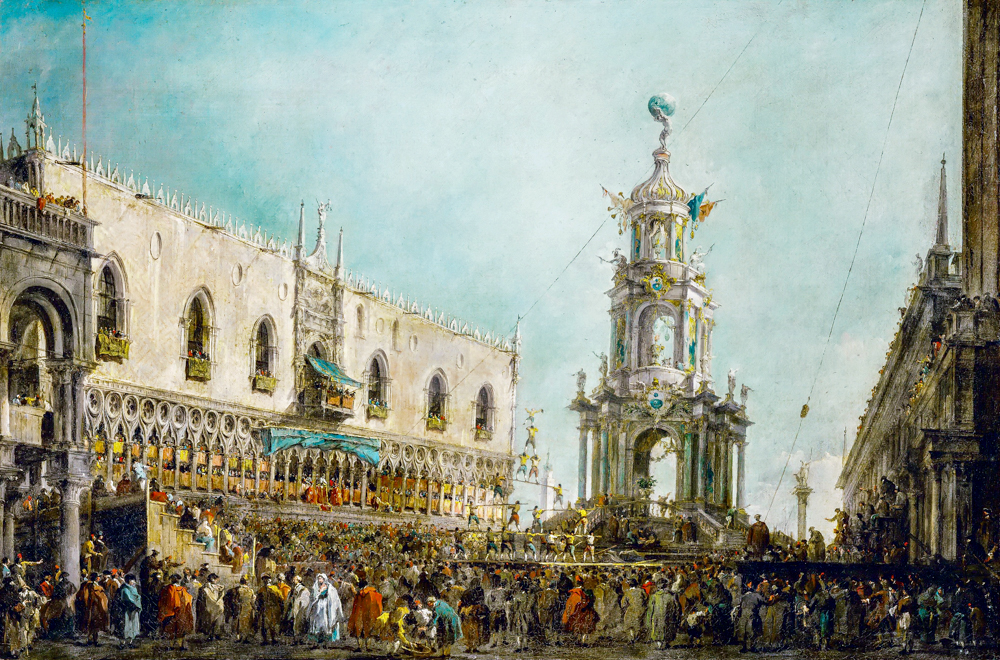

Francisco Guardi's "The Doge of Venice Helps Celebrate Easter on the Square"
Jean Antoine Watteau (France, 1684-1721) reflected the life of the upper class, where people wore dazzling silk and satin. The beautiful colors and intricate decorative styles in the painting replaced the more robust styles of the Baroque period, and the Rococo style began to emerge. Francois Boucher (France, 1703-1770)'s works have light themes, humorous styles, and often contain interesting content, representing the mainstream painting style of the Rococo period. Jean Honore Fragonard (France, 1732-1806) had a diverse range of expressive techniques, including delicate and delicate depictions of objects, rough and freehand depictions of shapes, and effective use of light and dark changes in his creations.
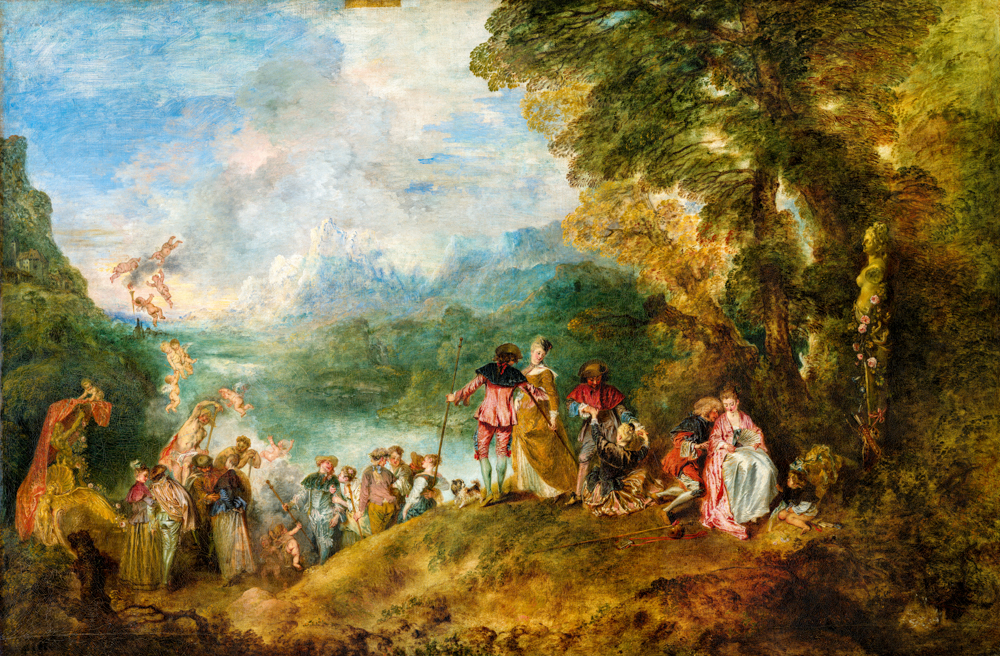
Jean Anthony Watteau's "Boating on the West Moss Island"
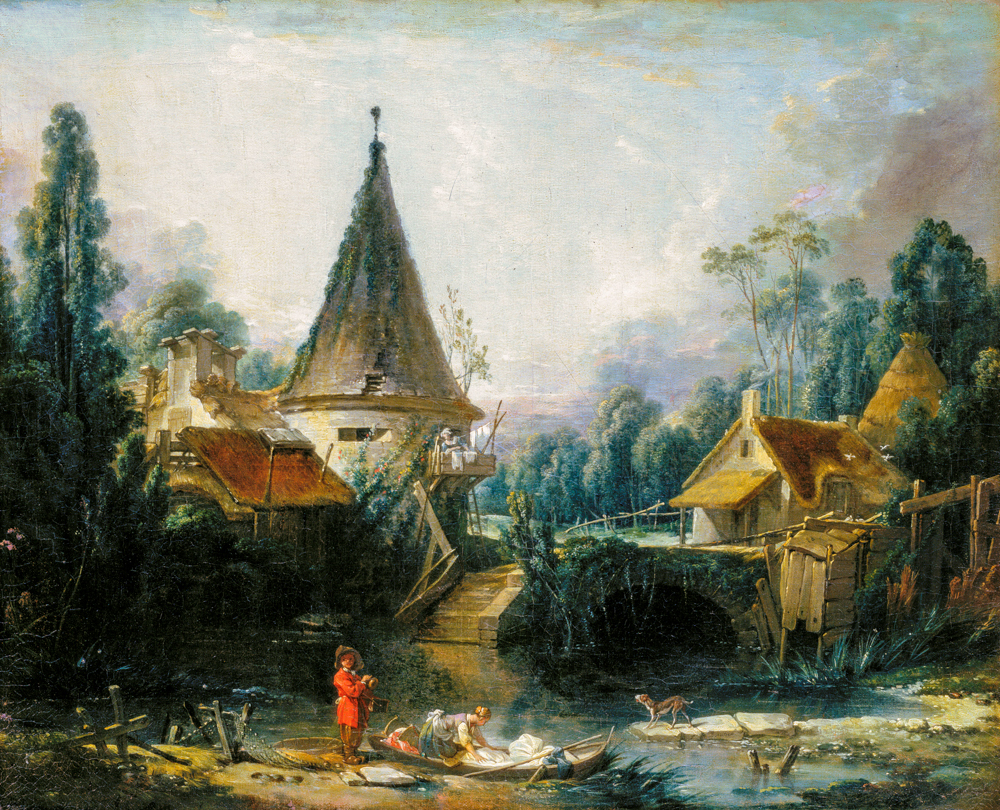

Francois Boucher's "Scenery near Beauvais"
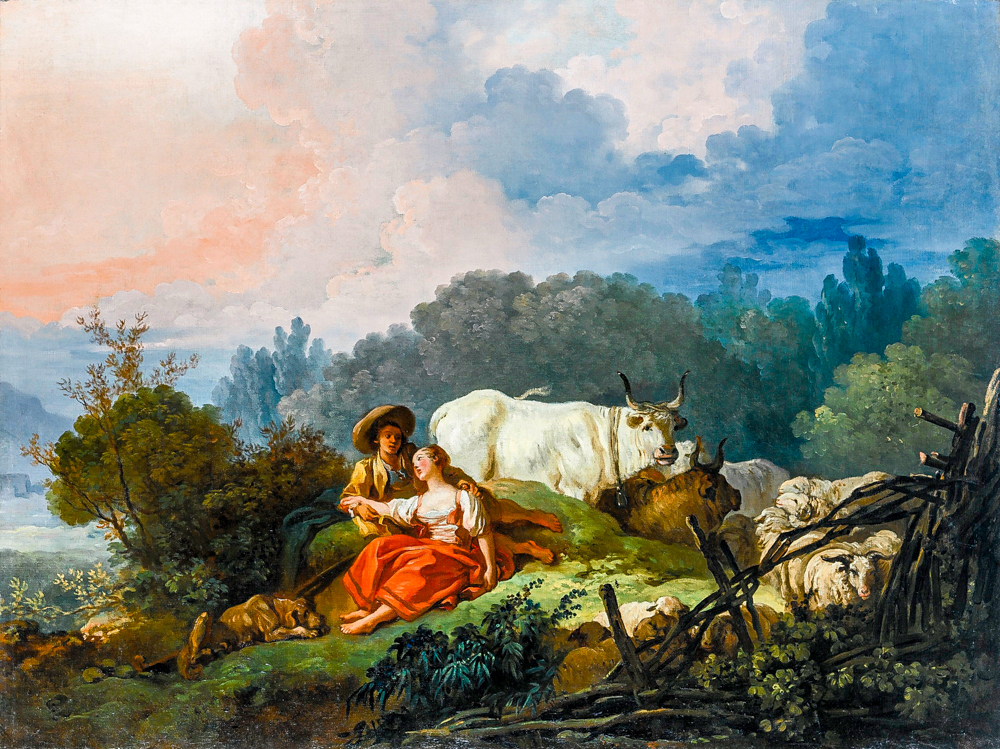

Jean Honor é Fragonard's "Pastoral Scenery of Shepherds and Shepherds"
Claude Joseph Vernet (France, 1714-1789) refined and elevated natural elements to present a unique decorative effect in his paintings. This effect not only reflects his artistic pursuit, but also showcases his profound insight into French harbor life. His painting style tends to be classical, and his later works have already shown a romantic style. Romantic landscape painter Joseph Mallord William Turner (1775-1851) was fond of depicting natural phenomena and disasters, and his interest in light and color exceeded form, laying the foundation for the formation of Impressionism in the future. He effectively promoted and elevated the status of landscape painting in the overall painting system. Caspar David Friedrich (Germany, 1774-1840) discovered new nature that people had not paid attention to, such as endless oceans or mountains, snow covered mountains, and sunlight and moonlight shining on these natural landscapes, conveying a noble spiritual power. Surrealists and existentialists both drew inspiration from his paintings. John Constable (1776-1837, England) used his brushstrokes and colors to depict something that cannot be conveyed through language in a specific light, time, or scene. He had an impact on the formation of the French "Barbican School" and the development of Impressionism. Ferdinand Victor Eugene Delacroix (1798-1863, France), who was skilled at using scenery to express painting language and inner emotions, called him the "father of modern landscape painting".

Claude Joseph Vernet's "Mountain View with Rivers"
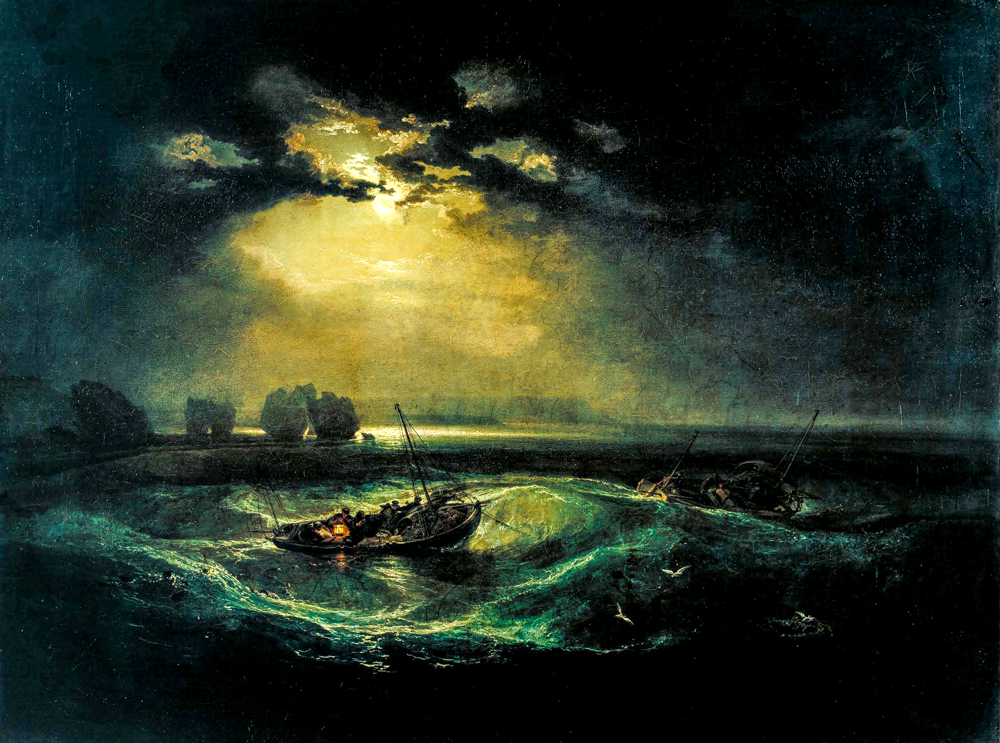

Joseph Mallord William Turner's "Fishermen at Sea"
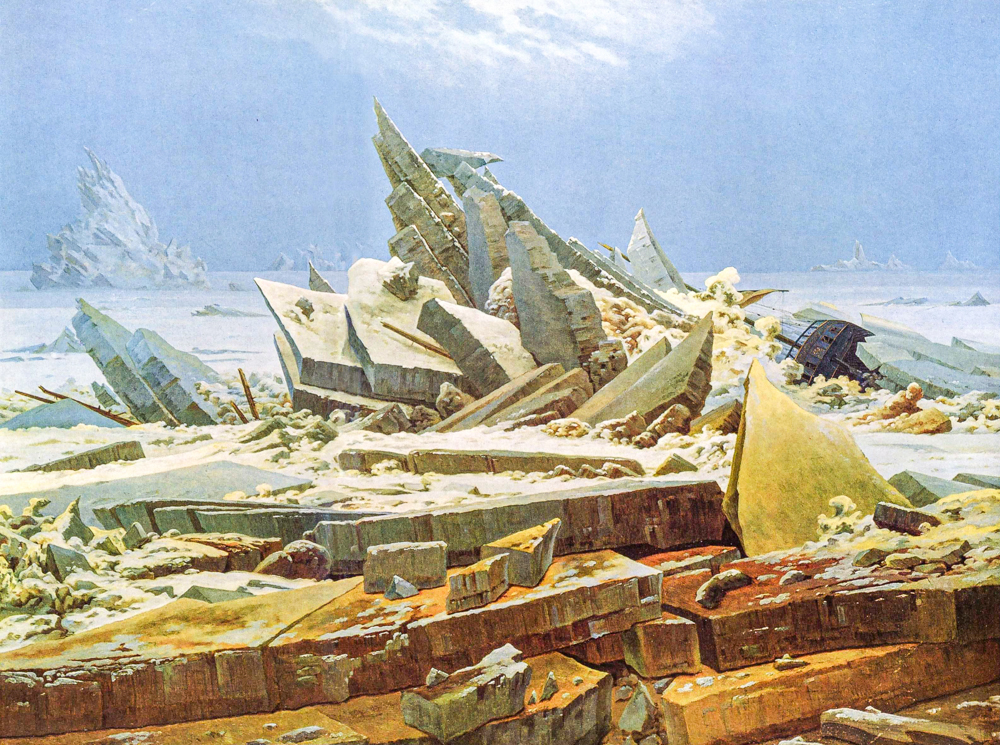

Caspar David Friedrich's "Ice Sea"
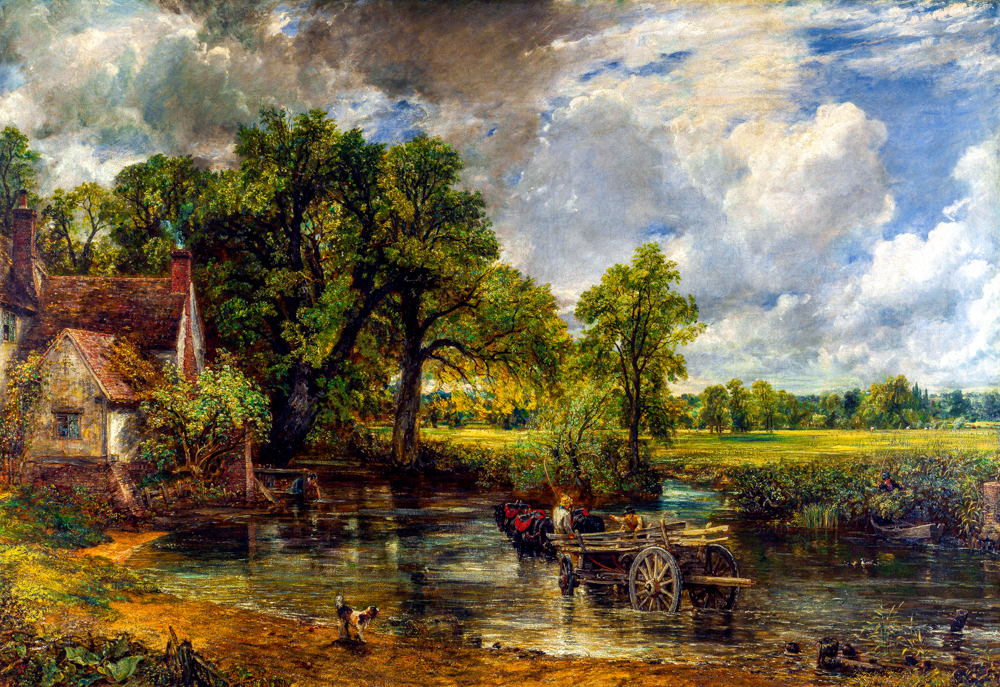
John Constable's Hay Cart
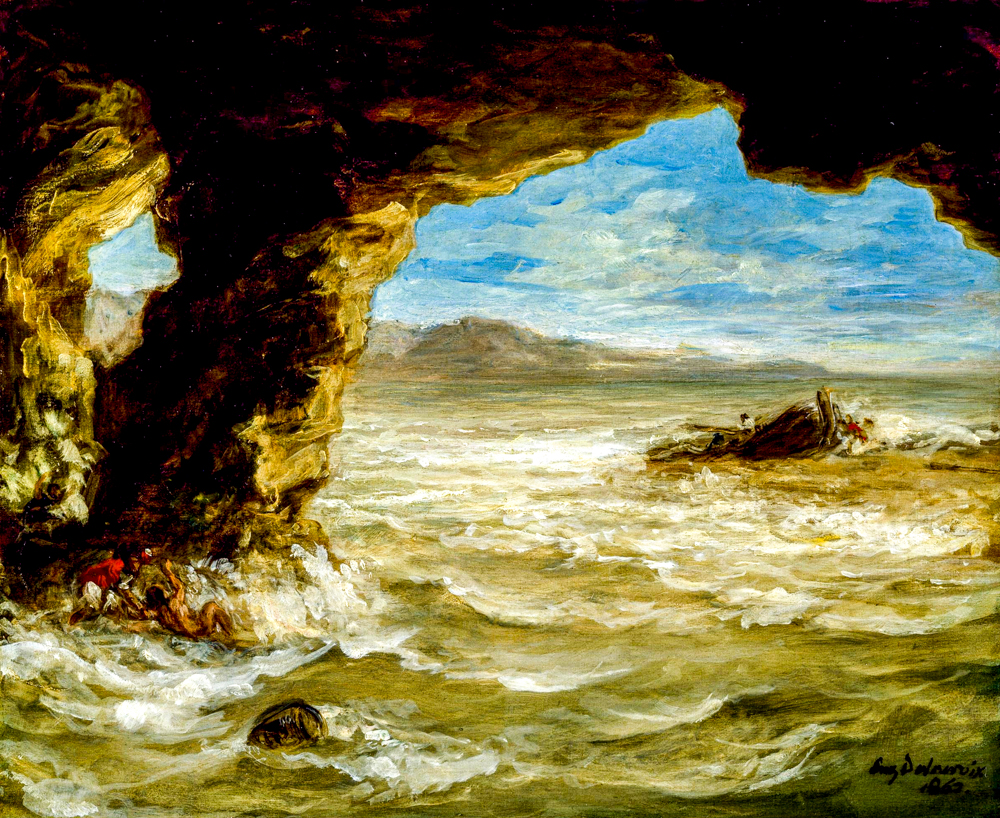

Ferdinand Victor Eugen Delacroix's' Sinks on the Coast '
Neoclassicism first appeared in the architectural and decorative design world of 17th century Europe. Due to the excavation of the ancient city of Pompeii in Rome, some painters hoped to revive the classical art of ancient Greece and Rome, thus abandoning the cumbersome decorative art of Baroque and Rococo styles. Starting from France, innovative designers used many new materials and techniques to reshape the elegant and dignified noble temperament contained in classical works. Corot Camille (France, 1796-1875), who depicted the simplicity and tranquility of rural France, went against the previous practice of painting the dark areas very dark. Instead, he worked hard to make the dark areas transparent and bright, greatly increasing the brightness of the entire painting. He is known as one of the three great landscape painters in France, along with Nicolas Poussin and Claude Lorraine.
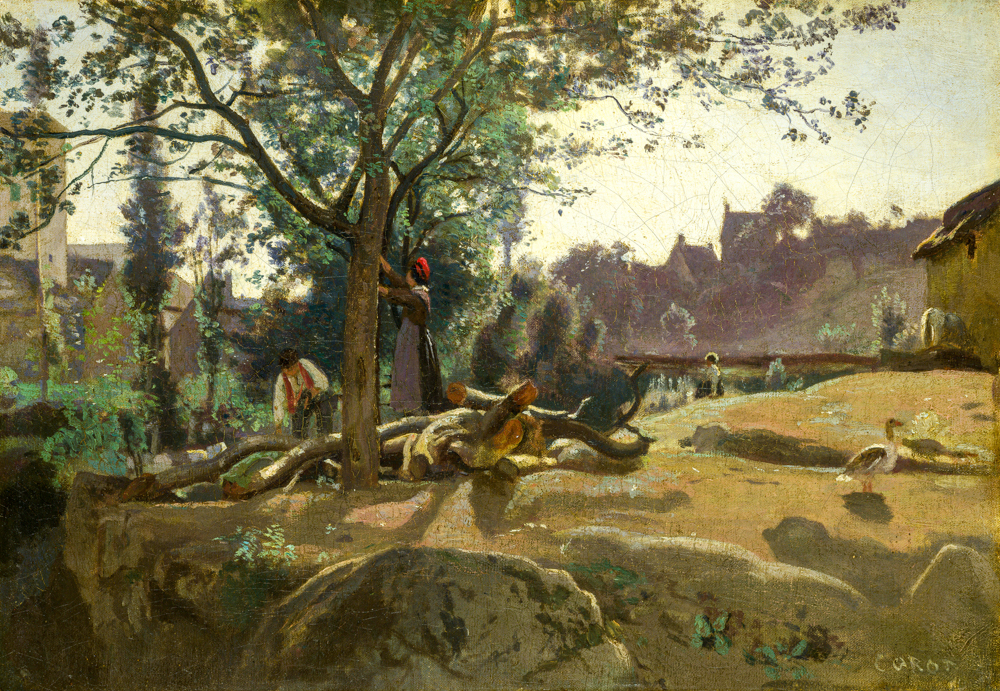

Camille Koro's "The Farmer Under the Tree"
In the 19th century, when French Neoclassicism and Romanticism were in opposition, painters living in the Babisson village of Paris went out of their studios to sketch in the wilderness, depicting colors that were closer to the true state of nature, forming the "Babisson School". It is also known as the "Fontainebleau School" because it is located near the Fontainebleau Forest. Jean Desire Gustave Courbet (France, 1819-1877), following Romanticism, opposed the artificiality and artificiality of official art, giving birth to the realism style and influencing Impressionism. Jean Francois Millet (France, 1814-1875), who was skilled in using light and color to express emotions and atmosphere, portrayed the dignity and beauty of the laboring masses through realistic depictions of their hard work, affirming their significance in art and opposing the erroneous notion that noble paintings must depict noble figures. Henri Julien F é lix Rousseau (France, 1844-1910) is regarded as a pioneer of the surrealist art style of the 20th century. He did not focus too much on the creation of perspective and light and shadow effects, and precisely because of this, the audience standing in front of his paintings were deeply moved. He once said, "Creators must have complete freedom to reach the realm of beauty and goodness in their thoughts. Charles Fran ç ois Daubigny (France, 1817-1878) walked out of his studio to sketch in nature, based on the realistic scenery of seeing as believing, emphasizing the richness of colors in the picture, and creating poetic and beautiful images. His works truly reflect the natural scenery and rural life of France, and have had a profound influence on Impressionist painters. He is known as the "Beethoven of water painting".
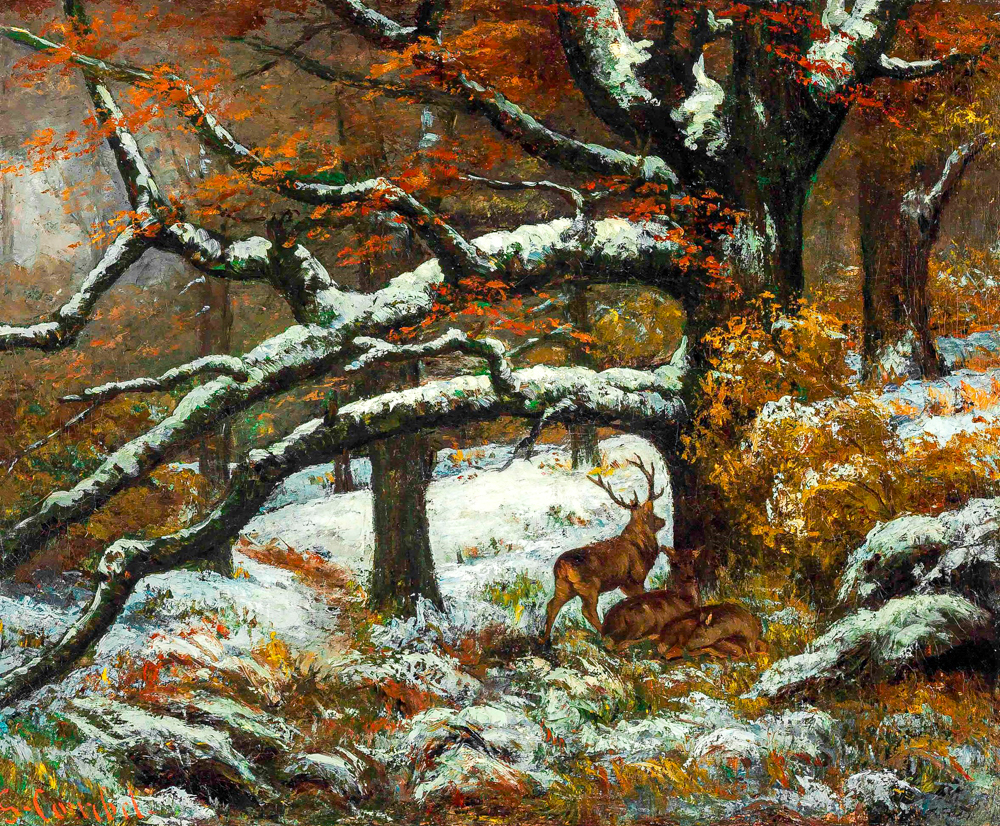

Gustave Courbet's' Lukang '
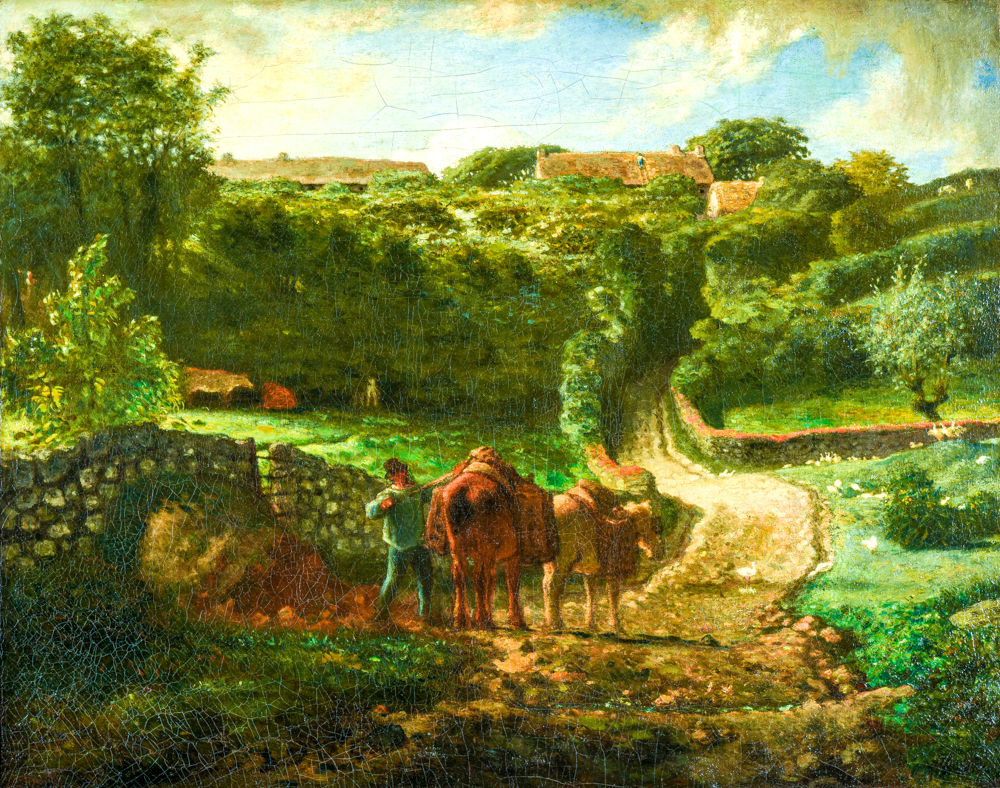

Jean Fran ç ois Miller's "Hameau Cousins of Greville"
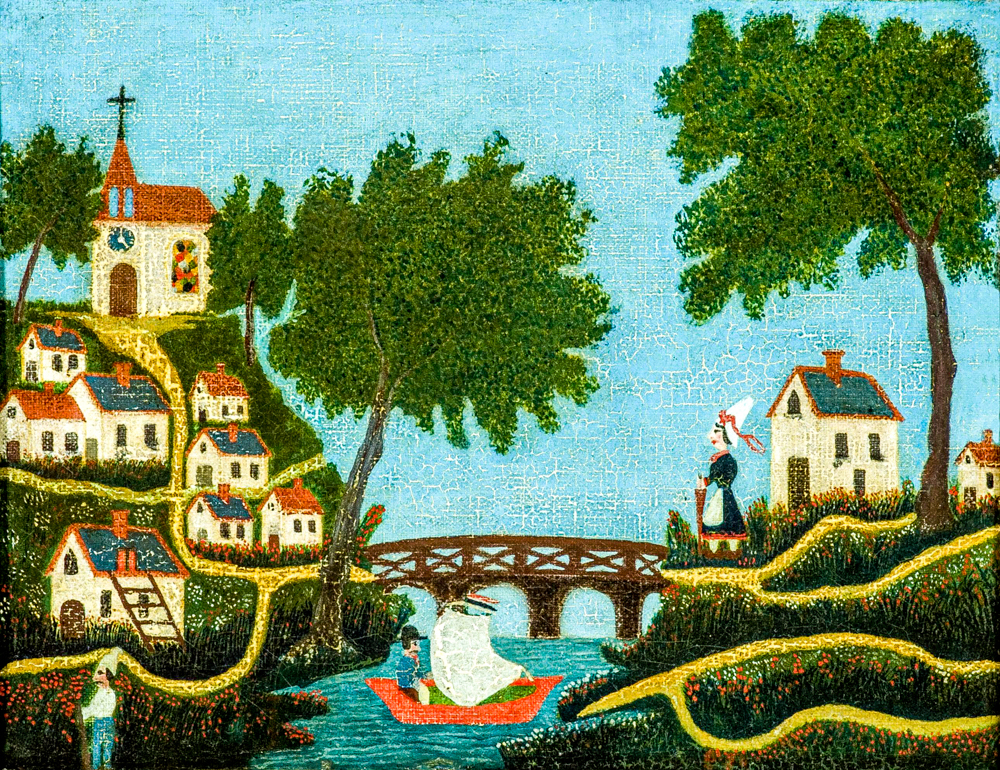

Henri Julian Felix Rousseau's "Scenery and Bridges"
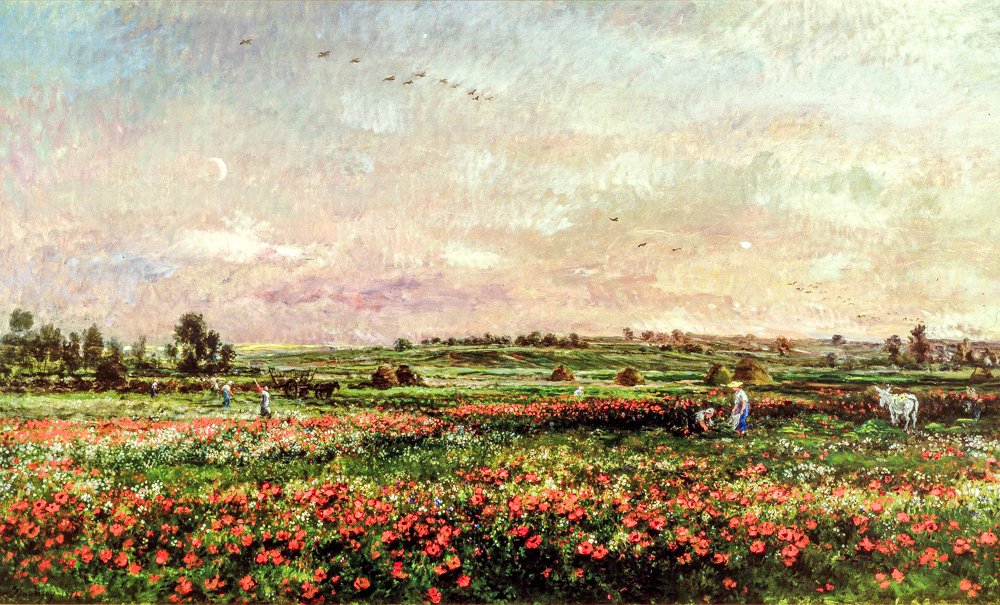
Charles Fran ç ois Dubigny's "The Fields of June"
Ryukawa Shixuan, the founder of ukiyo-e, is regarded as the creator of the art form known as "Roubi". His paintings mainly depict a constantly floating world. In the Edo period, the demand for art from the urban class increased, and Roubi gradually transitioned to woodblock ukiyo-e. Impressionism, Post Impressionism, and the Art Nouveau movement were all influenced by ukiyo-e. Katsushika Hokusai (Japan, 1760-1849) boldly absorbed the creative techniques of Dutch landscape painting on the basis of inheriting the style of Japanese famous scenic spots. He carefully observed the lifestyle and customs of Edo citizens, and his style was both abstract and pure, with techniques as simple as possible, thus creating a new style that combines Western techniques and Japanese tastes. Ando Hiroshige's landscape paintings (Japan, 1797-1858) often have bright colors, complex and symmetrical compositions, and a gradual sense of hierarchy in the picture. The close-up and distant views change slowly, giving people a poetic beauty.
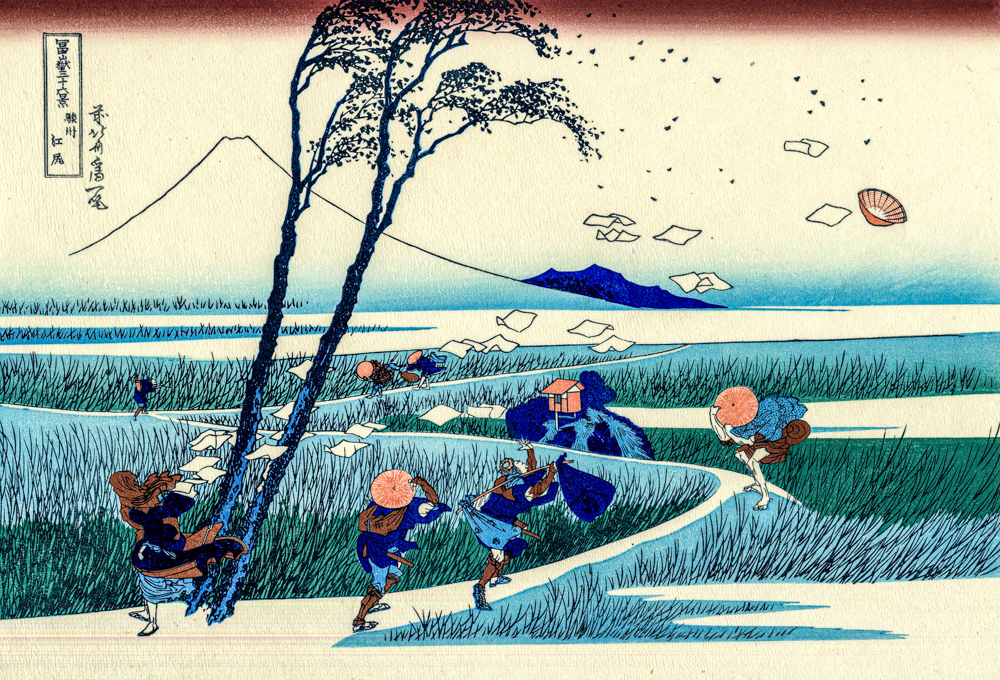

Katsushika Hokusai's "Junju Gangjiri"

Kagawa Hiroshige's "Kameido Umeko Shop"
Artists in the United States have left cities one after another to explore unknown nature, and this peaceful and vast natural scenery has brought spiritual comfort to the people after the Civil War. Some of the painters began to depict the scenery near the Hudson River, which became the beginning of the Hudson River School. Thomas Cole (England, 1801-1848) had a profound understanding of natural landscapes and romanticized them. Asher Brown Durand (1796-1886, USA), known as the "father of American landscape painting," had delicate painting styles and rich colors that were closer to the real natural world. As the United States developed the West, the second generation of Hudson River painters gradually began to pay attention to and depict the western regions of the United States. John Frederick Kensett (1816-1872, USA) had a conservative style and did not use bright colors or win over the wonders of the terrain. His works were characterized by light colors and mainly depicted calm headlands and water surfaces. Frederic Edwin Church (1826-1900) is renowned for his exquisite painting skills and unique depictions of magnificent natural landscapes. His works not only showcase the beauty and grandeur of the American continent, but also convey his reverence for nature. Albert Bierstadt (1830-1902, USA), who studied under the D ü sseldorf School for several years, created magnificent panoramic images through his meticulous depiction of tiny details and unique handling of light and shadow.
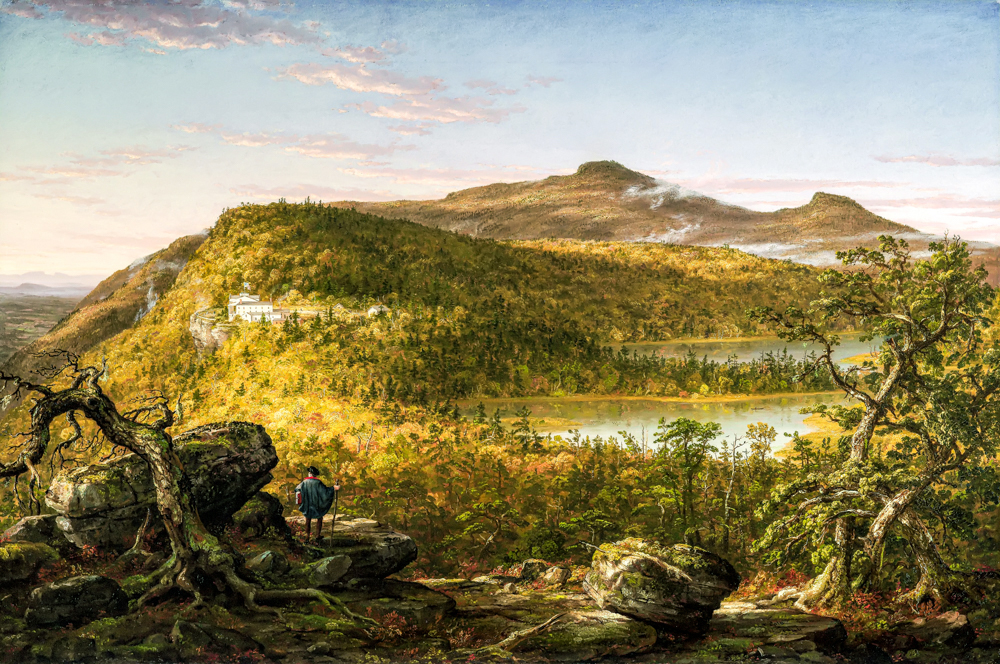

Thomas Cole's Two Lakes and Mountain Lodge in the Catskill Mountains
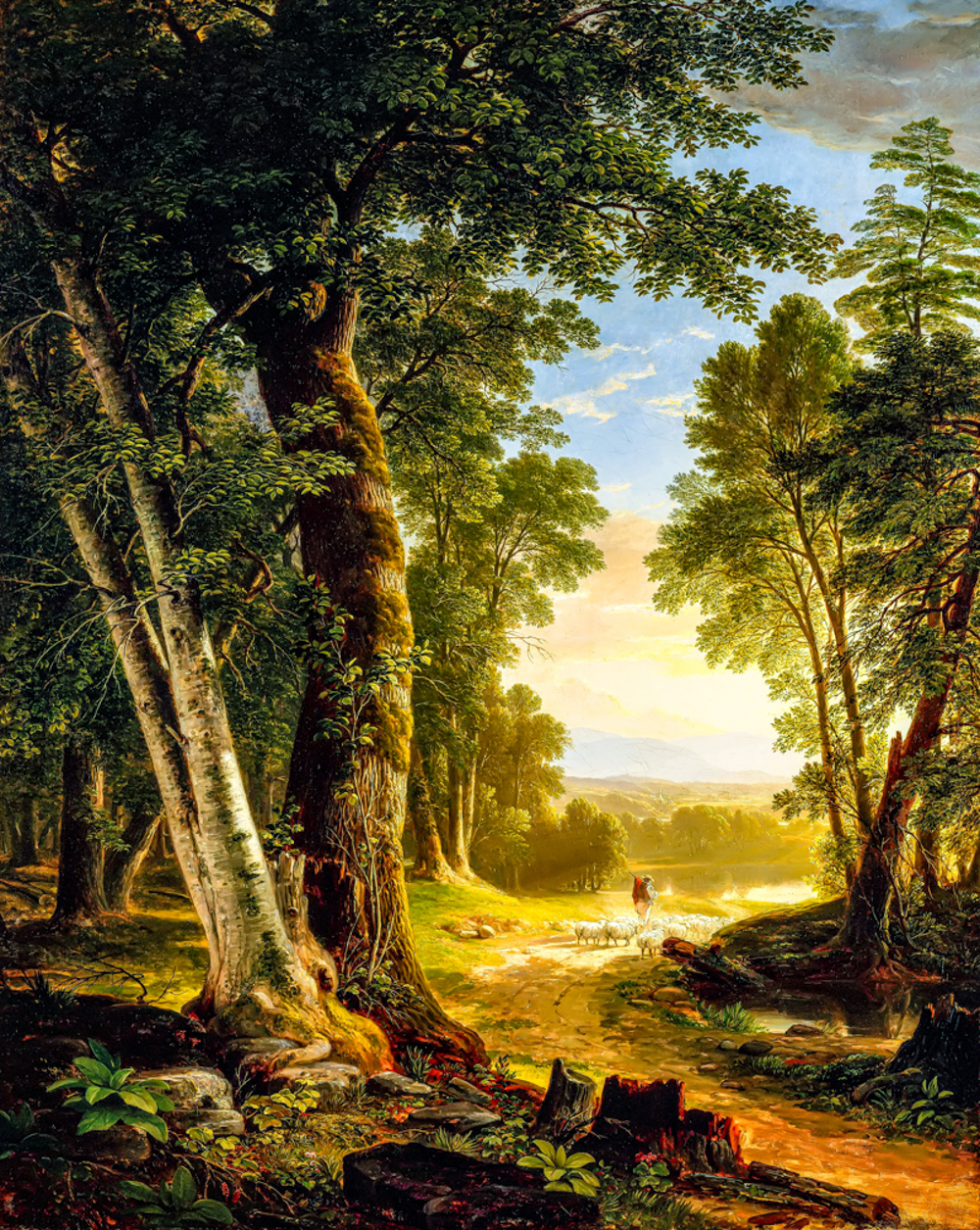

Asher Brown Durand's "The Beech"
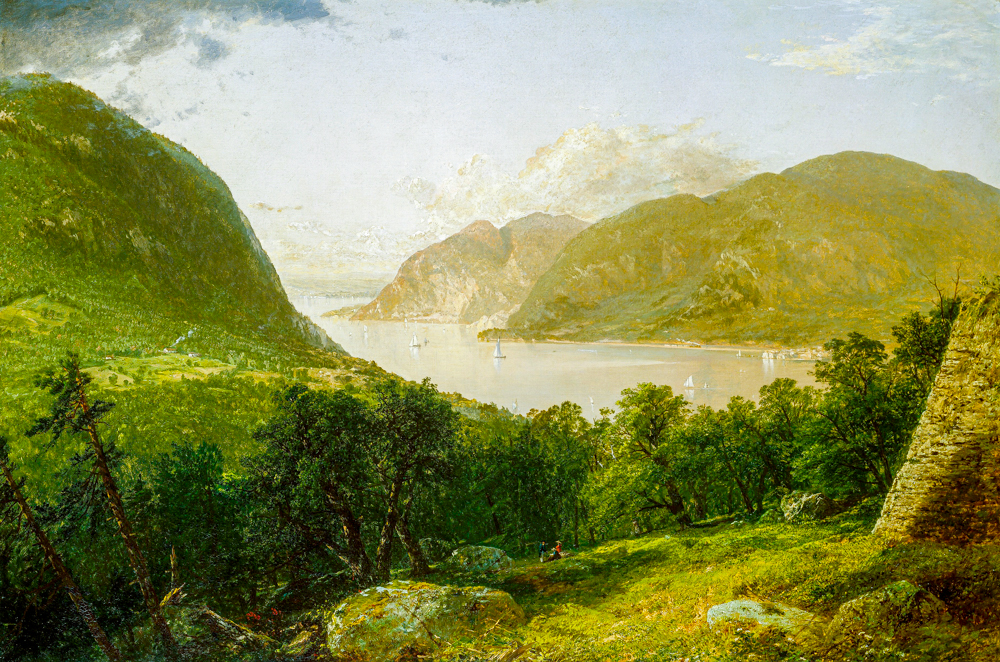

John Frederick Kenset's' Scenery of the Hudson River '
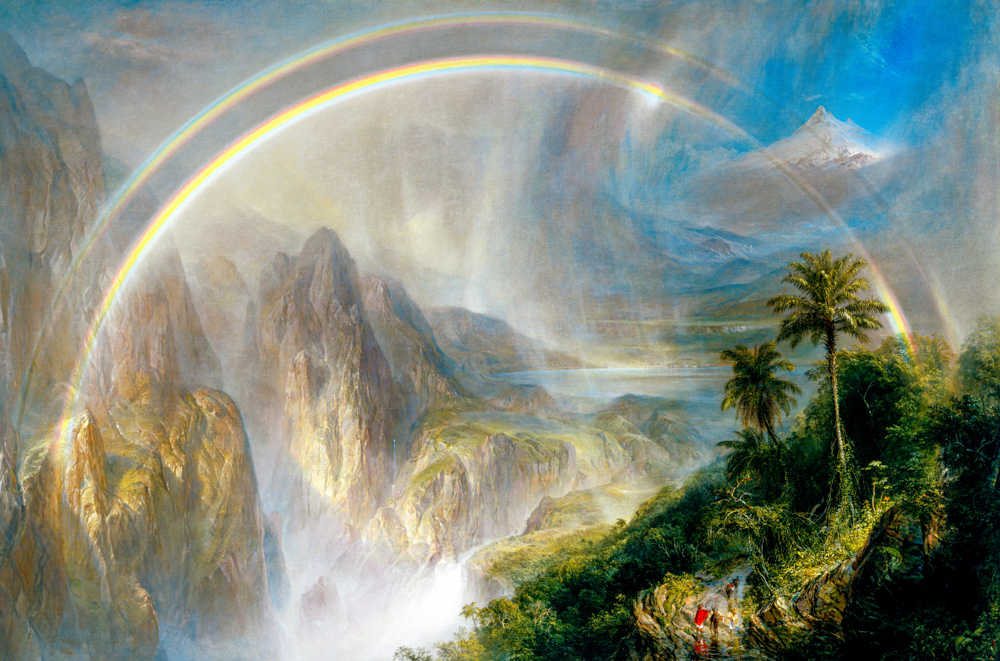

Frederick Edwin Church's "Tropical Rainy Season"
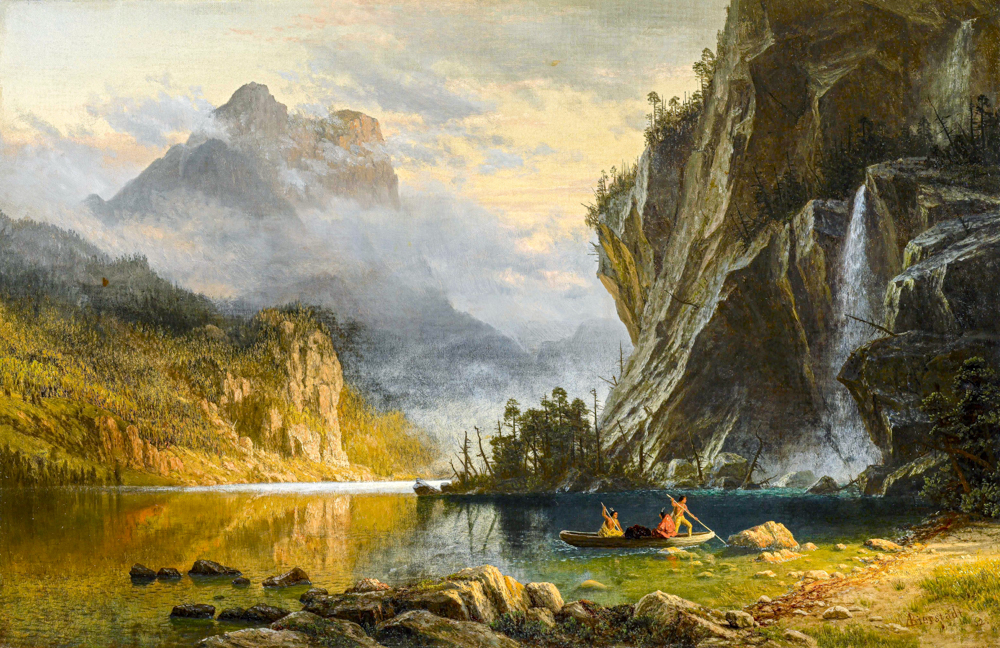

Albert Bierstadt's "Native Americans Fishing with Harpoons"
The Impressionism that emerged in France in the mid-19th century was an extension of realism. Impressionism strives to depict nature authentically, from realistic landscapes to understanding one's own value. The surface of the work pursues changes in light, shadow, and color, but in essence, it pursues the expression of one's own emotions. Camille Pissarro (France, 1830-1903) was influenced by the pointillist Georges Seurat and Japanese ukiyo-e styles in her early years, showcasing the beauty of nature through delicate light and shadow processing and vivid color expression, conveying people's love for life and nature. É douard Manet (France, 1832-1883) was influenced by the styles of Japanese ukiyo-e and Spanish painting, boldly adopting vivid colors and abandoning the traditional intermediate tones of painting. His painting style evolved from a three-dimensional three-dimensional space to a two-dimensional flat structure. Oscar Claude Monet (France, 1840-1926) was the first painter to use the technique of external light in his creations. He drew inspiration from the style of Japanese ukiyo-e in terms of color, and in his paintings, there were no very clear shadows or prominent or flat outlines. Through extensive artistic practice, he perfected the theoretical system of Impressionism. Alfred Sisley (France, 1839-1899) inherited the rigorous composition and subtle gray tones of the "Barbisson School". In order to improve the purity of colors and the brightness of the picture, he juxtaposed unadjusted colors on the canvas, allowing the audience to subconsciously blend adjacent colors together, resulting in rich color variations in the picture. Eugene Boudin (France, 1824-1898) often depicted the relationship between humans and nature in his works, with a particular preference for harbor and beach scenery themes. Lighthouse, sky, sea, and colorful crowds on beaches were frequently featured in his works. Gustave Caillebotte (France, 1848-1894) was skilled at capturing the variations of light on different objects and the subtle differences in color under the illumination of light, which gives his works a high visual impact and makes the audience feel as if they are in the scene of the picture.
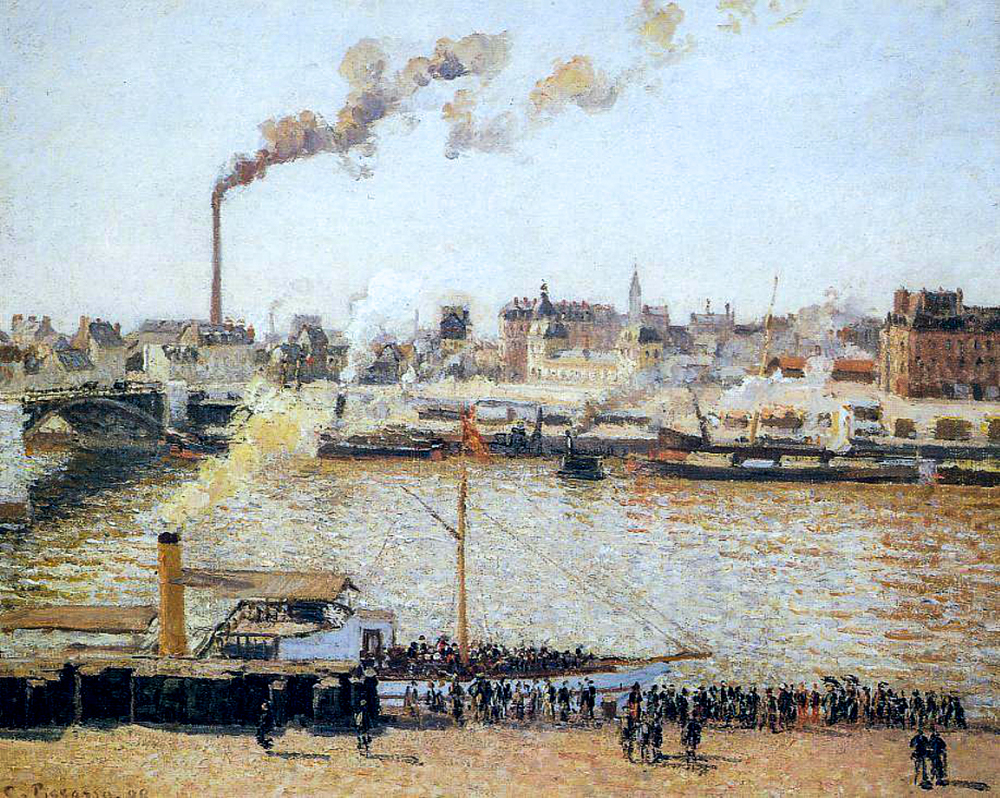

Camille Pisaro's "Scenery of Rouen"
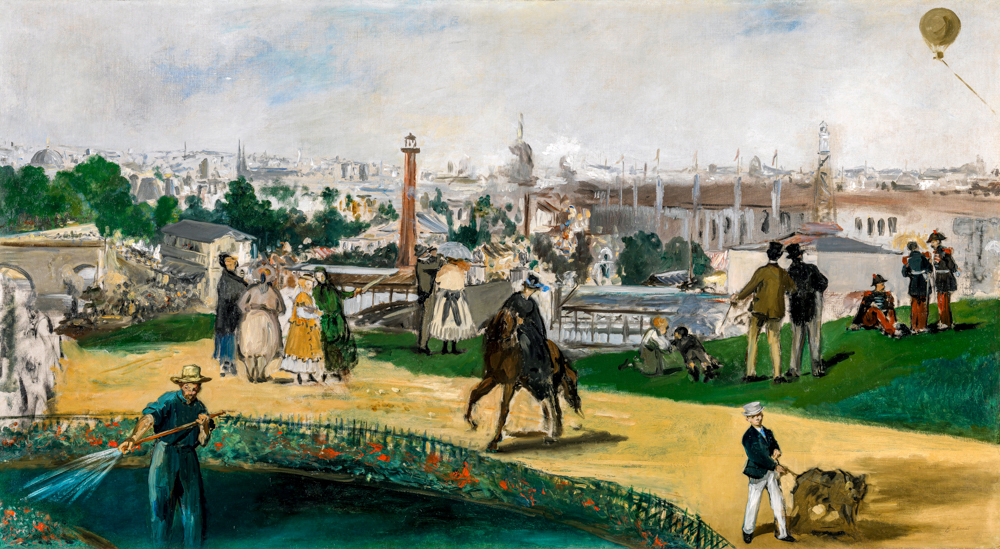

Edward Manet's "1867 World's Fair"

Oscar Claude Monet's' The Blooming Arch '
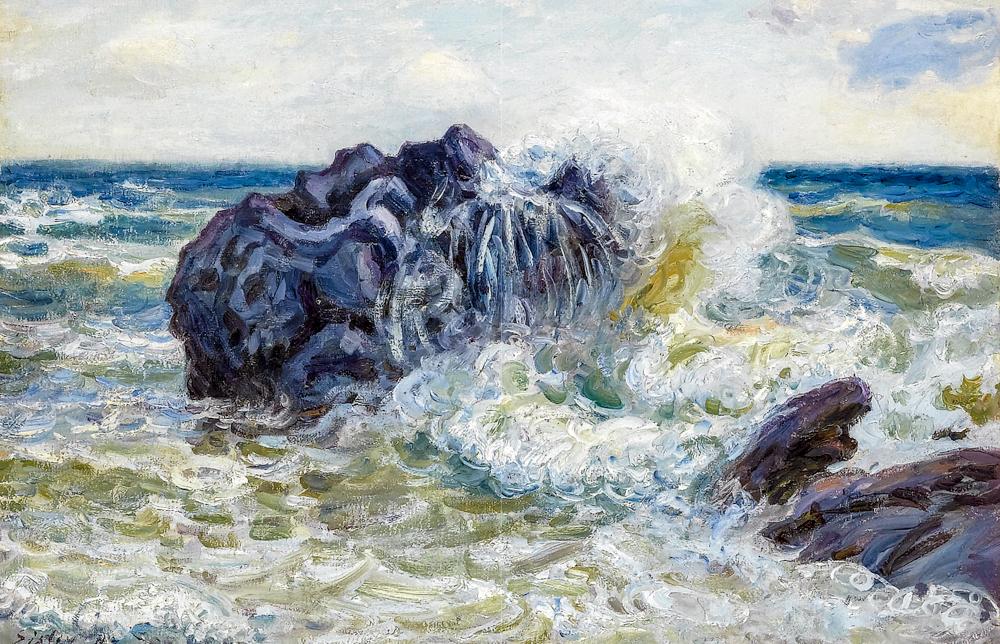

Alfred Sisley's' A Pile of Rocks in Langland '
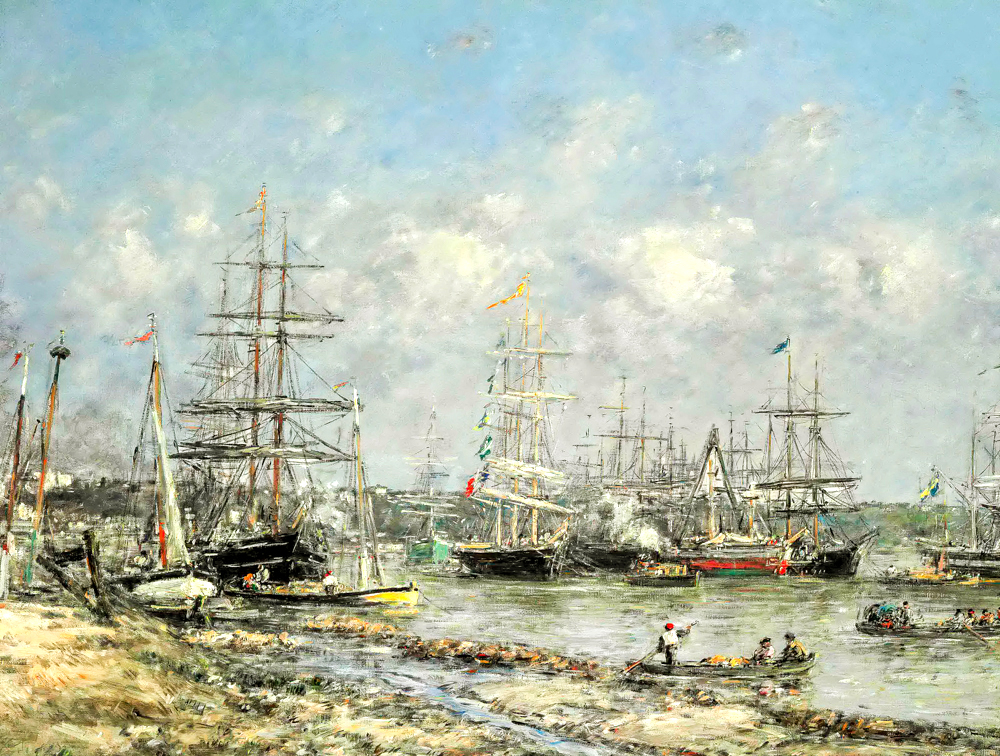
Eugene Boudin's' Port of Bordeaux '
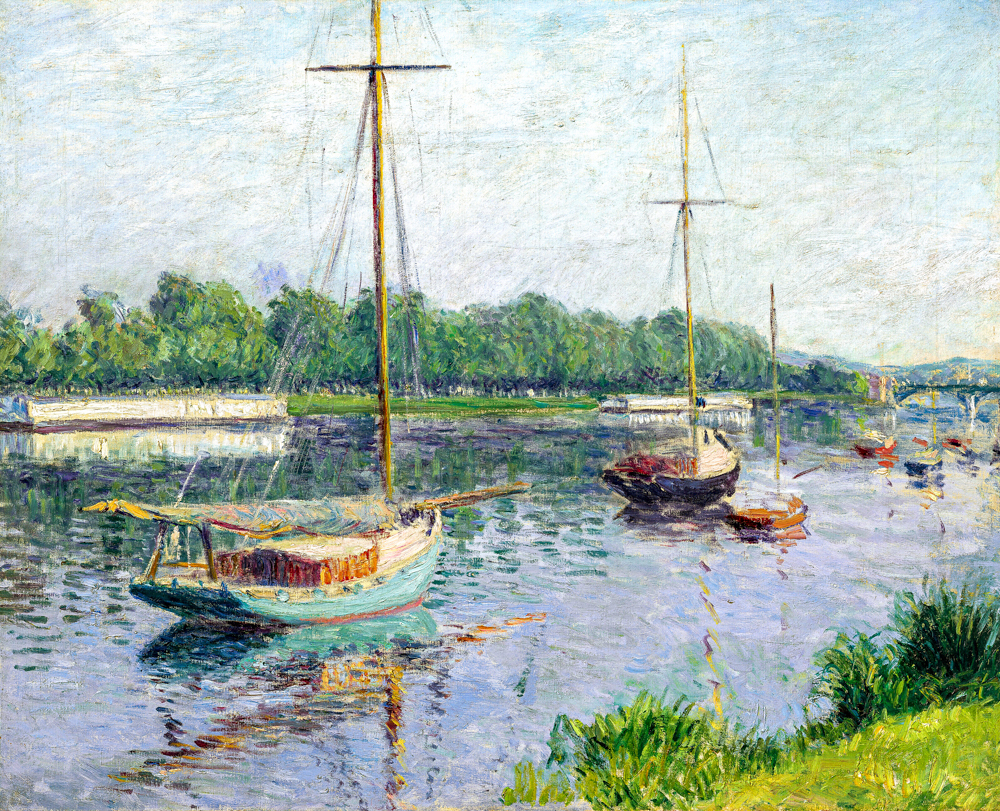

Gustav Caillebott's "The Argenteuil Basin"
Symbolist Gustave Moreau (France, 1826-1898) blended the techniques of classicism with the passion of romanticism, possessing both the traditional modeling abilities of classicism and the ability to use gorgeous and brilliant colors. Moreau said, "I neither believe in what I can touch nor what I can see, I only believe in what I cannot see or touch." Pierre Puvis de Chavannes (France, 1824-1898) used symbolic techniques to express mythological and religious content, using metaphors or hints to convey ideas and emotions, and his works were bright, stable, and decorative in color. Odilon Redon (France, 1840-1916), also known as the "Prince of Dreams," juxtaposed real-life objects with objects in the dream world, allowing viewers more freedom to appreciate the suggestive nature of the work.
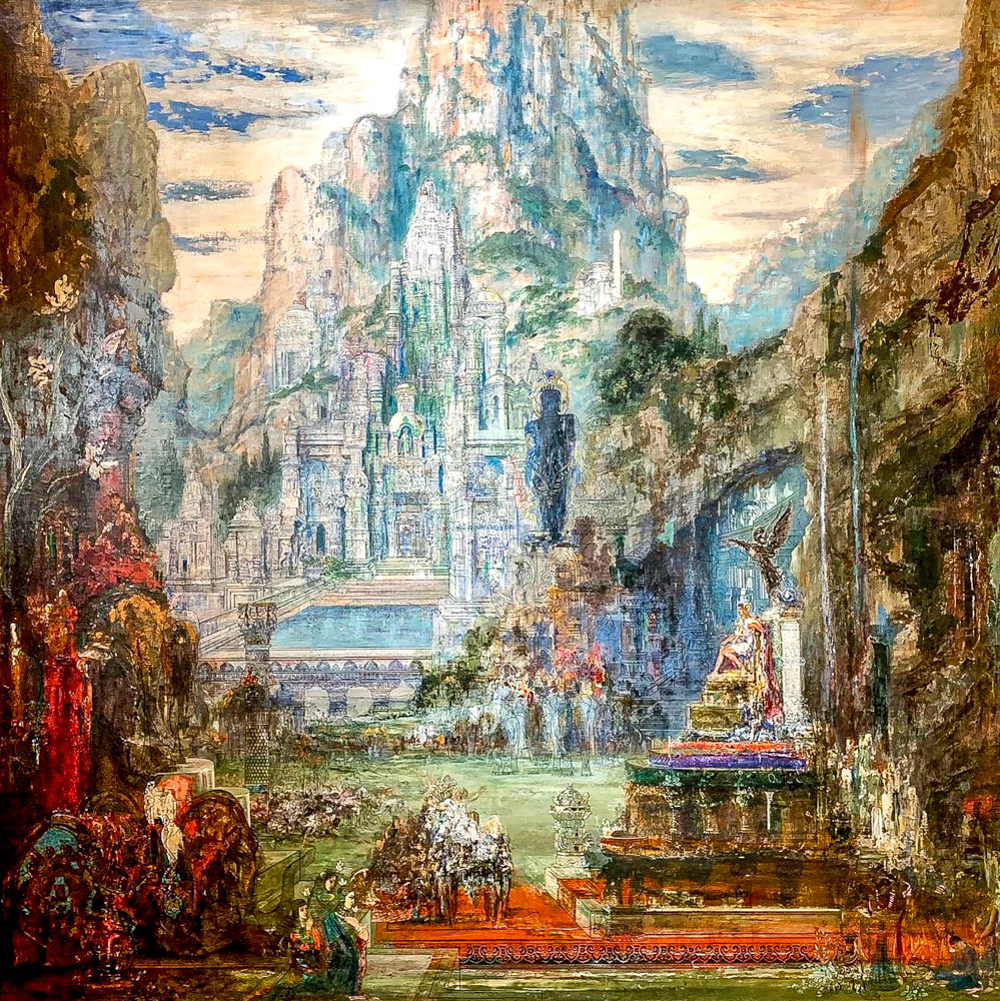

Gustav Morrow's Victory of Alexander the Great
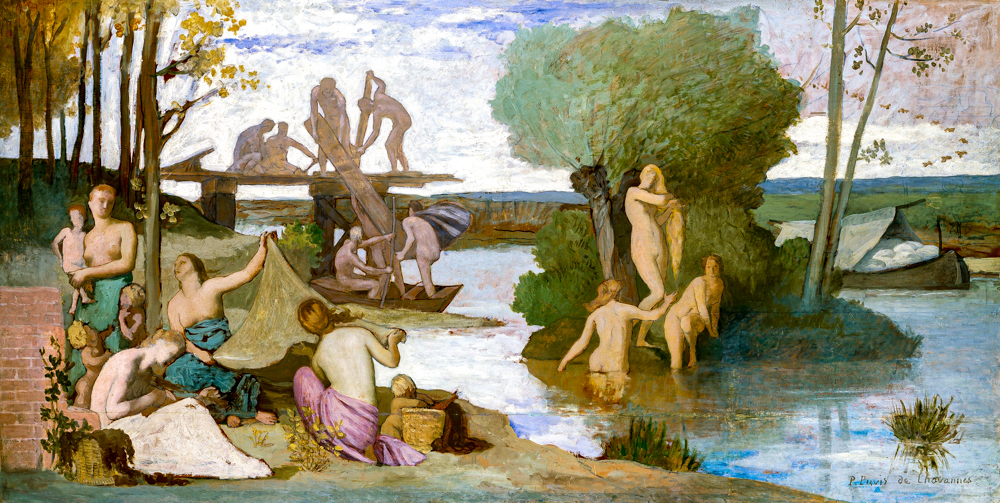

Pierre Pivi de Chavanna's "The River"
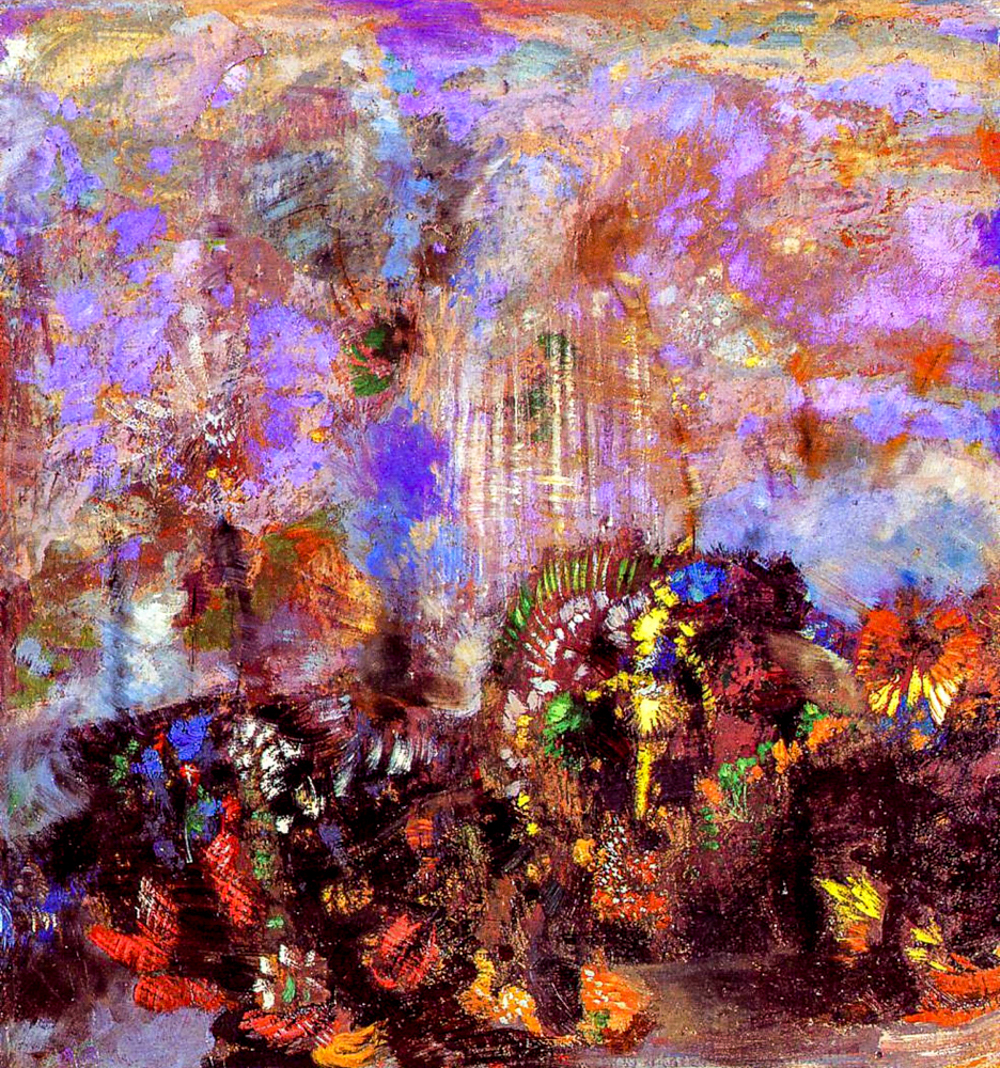
Odilon Redon's "Flower Composition"
The history of Western art refers to painting before Paul C é zanne (France, 1839-1906) as traditional painting, which emphasizes the authenticity and objectivity of the depicted scene, pays attention to the proportion between elements, the perspective relationship of the picture, and the anatomical structure of the human body, and is a representation of reality or nature; Subsequent non-traditional paintings, such as the Post Impressionist style, focused on the composition of the image or the expression of the artist's own spirit and ideas. Paul C é zanne attempted to explore a simple form of expression beneath natural appearances, organizing the scattered visual images in front of him into ordered images. He believed that the painting language of Impressionism, which blurred objects, would not be able to form the meaning of the picture, emphasizing the clarity and solidity of objects. His ideas influenced the painters of Cubism and Abstraction, and he was known as the "father of modern painting". Paul Gauguin (France, 1848-1903) was initially fascinated by the Impressionist art style, but later influenced by the aesthetic concepts of symbolism, he transcended naturalistic observation and pursued emotional expression. He wrote, "Impressionists blindly study color without any freedom, they only focus on the eyes, and are indifferent to the mysterious core of thought, thus falling into a state of only scientific reasoning." His painting style has a tendency towards primitiveness and symbolism, and influenced the "Nabi School" with his synthesis style and bold color methods. Vincent van Gogh (Netherlands, 1853-1890) did not focus on the representation of objective objects, but rather on the expression of the inner feelings of things, thus exploring a expressive painting language. In 1889, after arguing with Paul Gauguin, Vincent Wilhelm Van Gogh cut off his own ear and was sent to the St. Remi Asylum. In 373 days, he completed over 150 oil paintings and more than 100 sketches. At this time, his painting style had become expressionist, and the images that were like waves and flames were full of melancholy and sadness. Georges Seurat (France, 1859-1891) paid special attention to optical and color theory and conducted extensive experiments dedicated to methodological and theoretical research. Some believe that his death marked the end of Neo Impressionism.
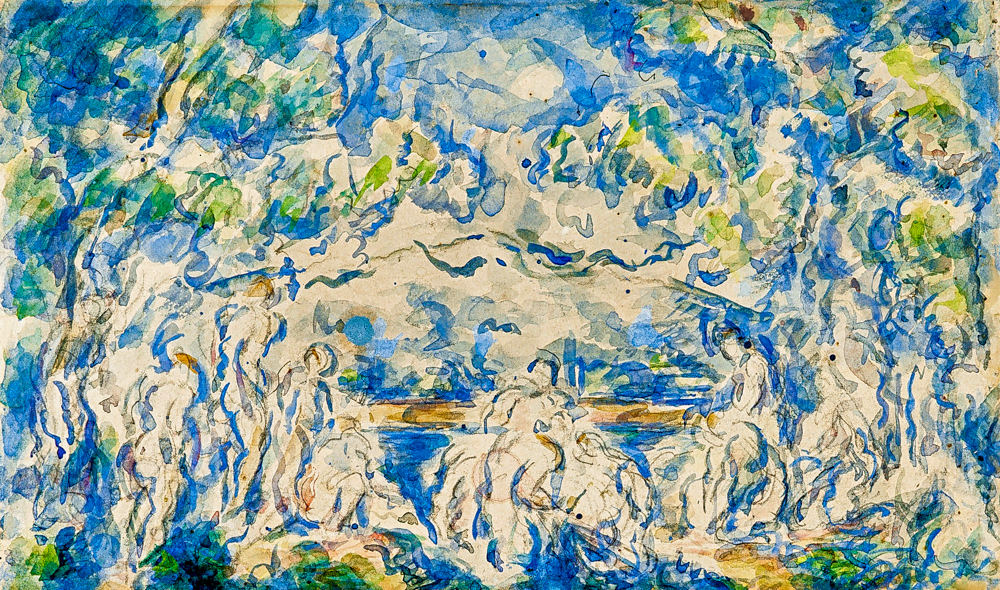

Paul C é zanne's "Bathers Against the Background of Mount Saint Victor"

Paul Gauguin's "The Woman on the Riverbank"

Vincent Wilhelm Van Gogh's "The Blooming Orchard"
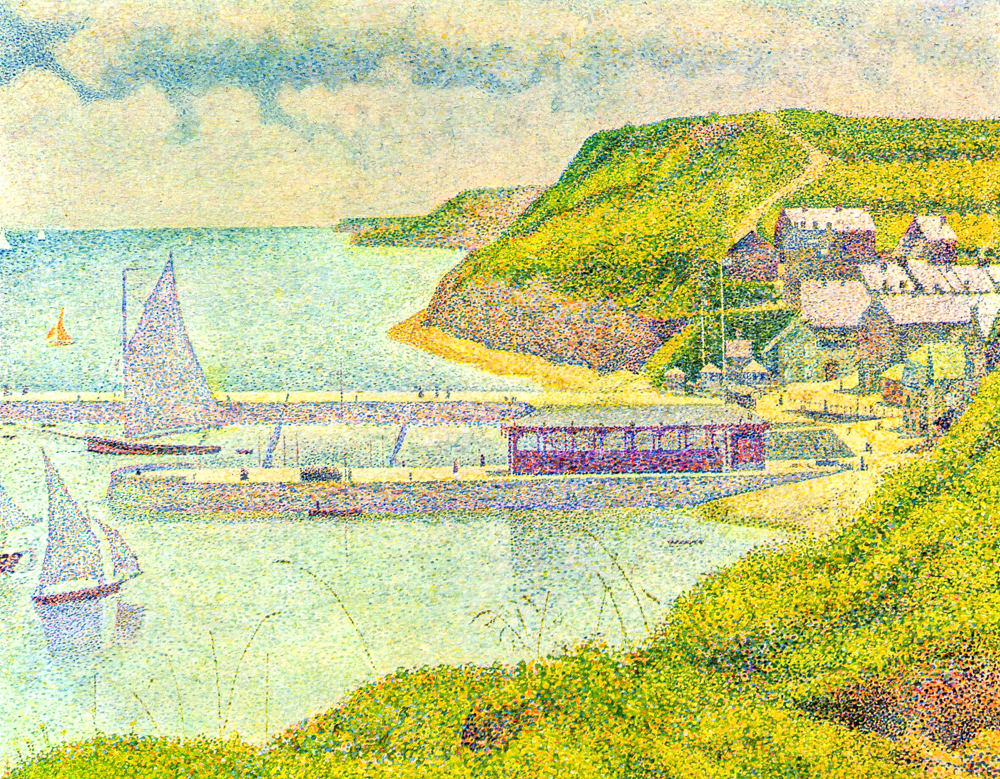
George Shura's' Port Besan '
The painters of the "Nabi School" proposed the creative theory of "double adjustment", which objectively adjusts based on pure aesthetic theory, decorative concepts, and composition techniques, and subjectively adjusts through the painter's own intuition. Pierre Bonnard (France, 1867-1947) combined brilliant colors and varied structures to form a unique subjective art, attempting to explore the relationship between colors and tones in nature, emotionalizing and impressionizing the real world, and blending self experience recognition through "synesthesia", surpassing the visual reality of the real world. Paul Serusier (France, 1863-1927) used flat painted surfaces, strong contour lines, and subjective colors to depict summarized and simplified forms, giving painting a strong sense of rhythm and decoration. He was a pioneer of abstraction and a source of inspiration for the Nabis movement, synthesism, and cloisonn é (separation). Interior oriented leader É douard Vuillard (France, 1868-1940) used Impressionist techniques to depict the daily lives of relatives and friends indoors, in Parisian gardens, and on the streets. His creations did not rely on central perspective, but relied purely on subjective intentions and decorative concepts to create a sense of form. Maurice Denis (France, 1870-1943), who painted decorative murals for churches, combined peaceful sketches with bright colors, and harmoniously matched blue and rose colors to create a solemn atmosphere and beautiful light and shadow in the painting.
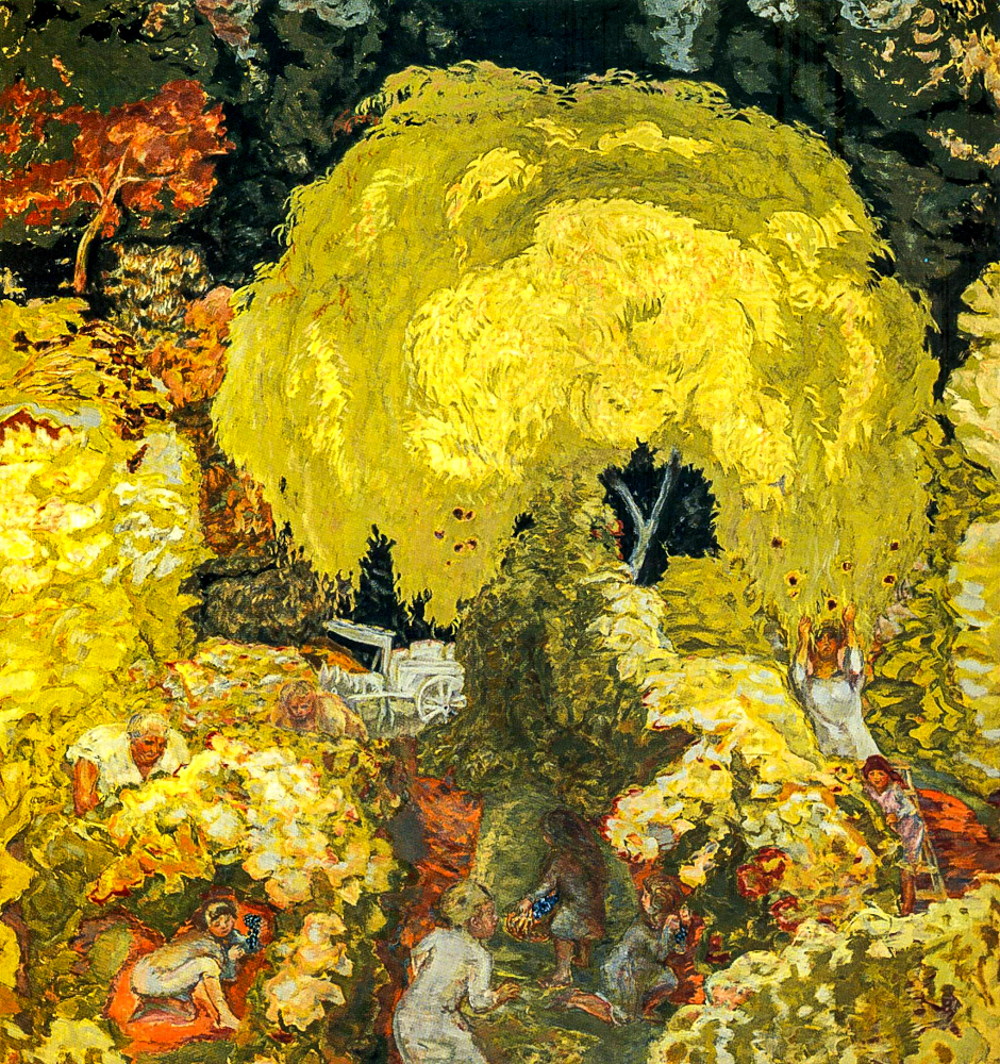

Pierre Bonnard's "Autumn: Fruit Pickers"
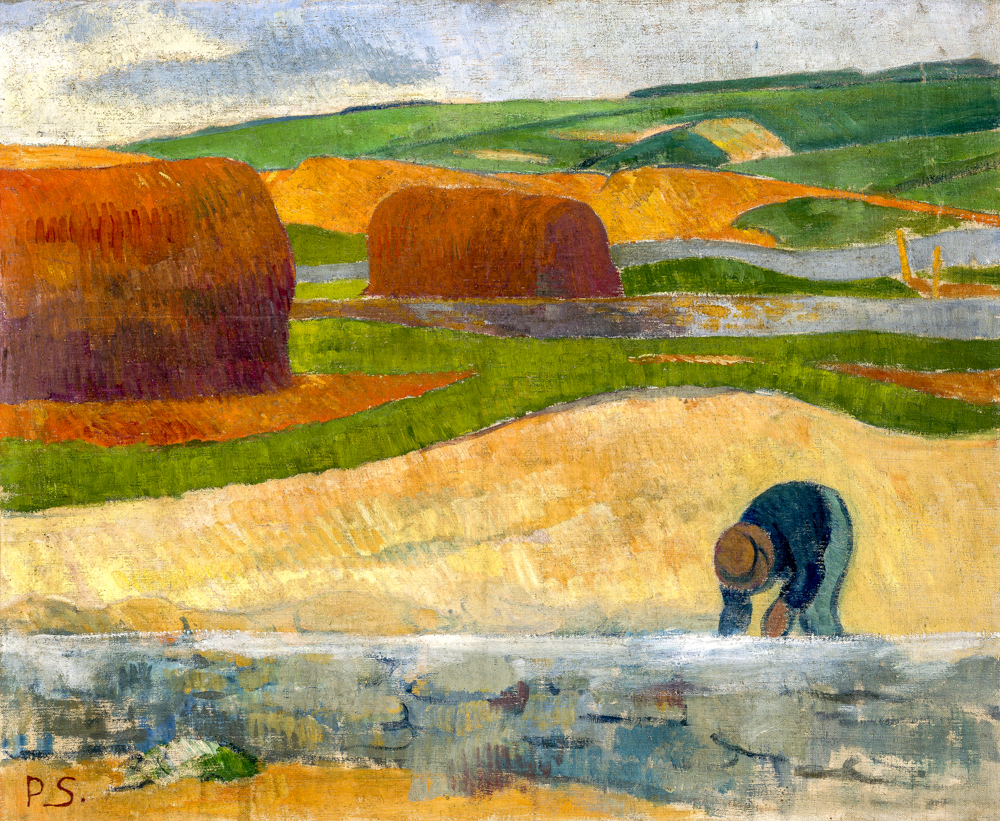

Paul Serusier's "Seaweed Collector"

Virgil Edward's "Painting with a Wild Chicken"

Maurice Dennis' The Waves'
At the end of the 19th century, the "Fauvism" was prevalent in France, where painters used bright and heavy colors and crude brushwork to create strong visual effects, showing an expressionist tendency to pursue emotional expression. Maurice de Vlaminck (France, 1876-1958) and Andr é Delang were immersed in the study of color all day long in their early days. Together, they created the "Shatt School" as the source of "Fauvism". He said, "I increase the brightness of all colors and transform everything I feel into a solid colored orchestral piece." Edvard Munch (Norway, 1863-1944) often used themes such as life, death, love, terror, and loneliness, expressing his feelings and emotions through contrasting lines, color blocks, concise and exaggerated shapes. His painting style influenced the formation of expressionism in Germany and Central Europe. The sentence is:. Henri Matisse (France, 1869-1954) was skilled at extracting high-purity colors from natural objects and combining flat color blocks according to certain internal needs to create a musical rhythm. He said, "I use color as an expression of emotion, not as a plagiarism of nature." Andr é Derain (France, 1880-1954) regarded color as the soul of painting and used subtle and elegant cool tones as the main color used in his creations. He gave up the subjective expression of expressionist style and devoted himself to establishing a mutually dependent and interwoven relationship with objects. He once said, "Realism has become... It's over, and painting has just begun. Albert Marquet (France, 1875-1947) conducted in-depth research on traditional art and was influenced by the art trends of the time. His painting style began to transition from Impressionist style to Neo Impressionist style, with the use of pointillism. The "Fauvism" style originally portrayed in his works was abandoned, and he pursued a sense of space with different levels of brightness. Georges Rouault (France, 1871-1958) gradually developed his own artistic style through his contemplation of society and religion. His themes were expressed through bold thin strokes of dark red and blue, creating strong contours that created a rather melancholic and gloomy image. In his later years, his painting style was mostly thick strokes, with vibrant tones and thick lines used to outline the image. Henri Charles Manguin (France, 1874-1949) did not use straight lines to depict themes in his paintings, but instead used clever curves that were coherent and coordinated between lines, implying and outlining shapes through colors, and the ups and downs of shapes in his paintings brought about color changes. Raoul Dufy (France, 1877-1953) loved to depict nature and life straightforwardly, exuding an elegant and agile temperament. Through lively brushstrokes, he exaggerated and deformed objects, pursuing decorative effects.
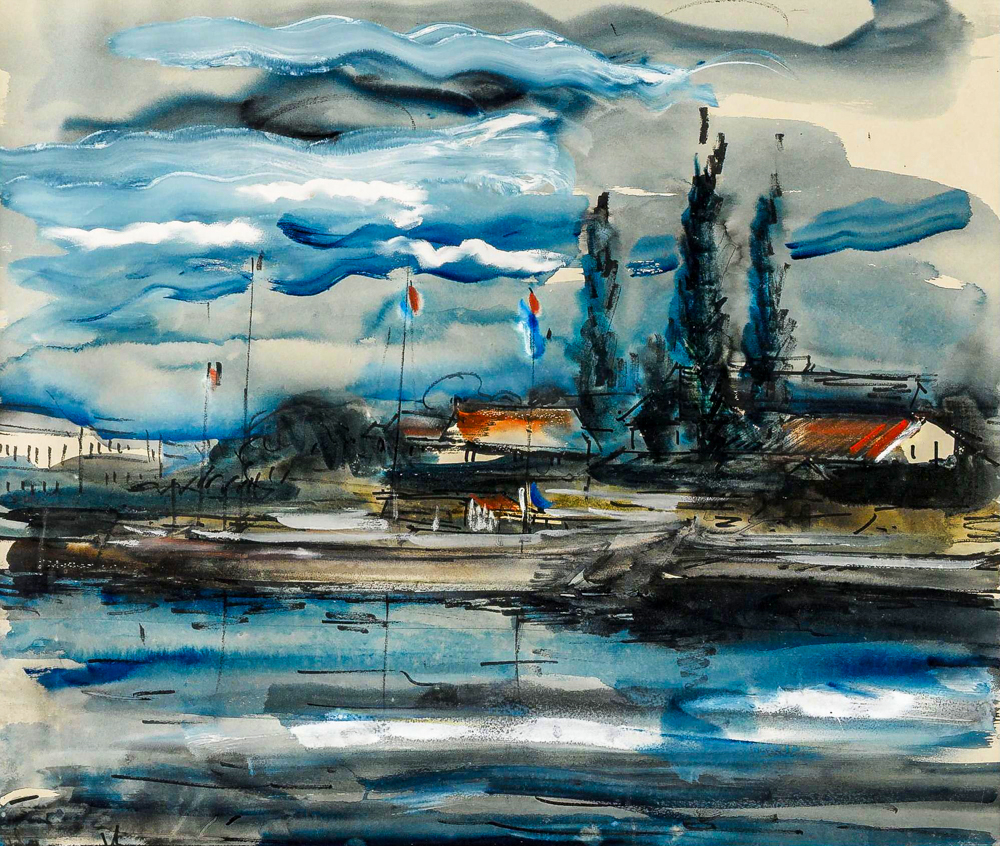

Maurice de Flamenco's "Scenery by the River Earl"
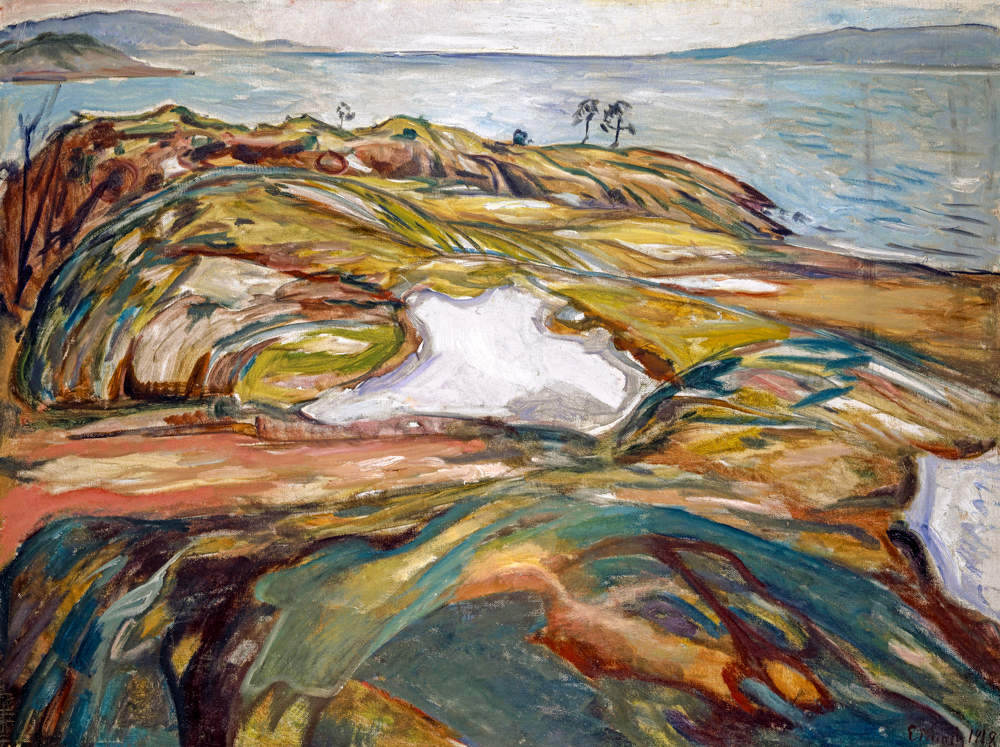

Edward Monk's' Coastal Scenery '
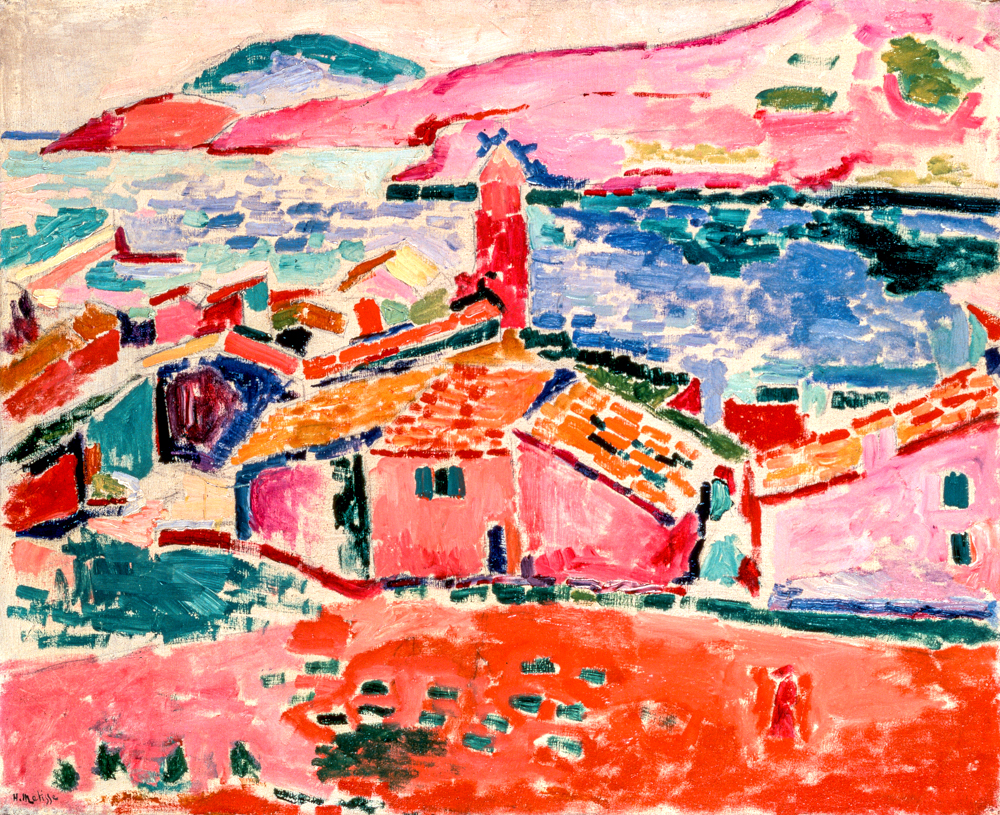

Henri Matisse's' Scenery of Corleone '

Andr é Delang's' Lot Valley '

Albert Marquardt's "The Port of Olonne in Les Sables"
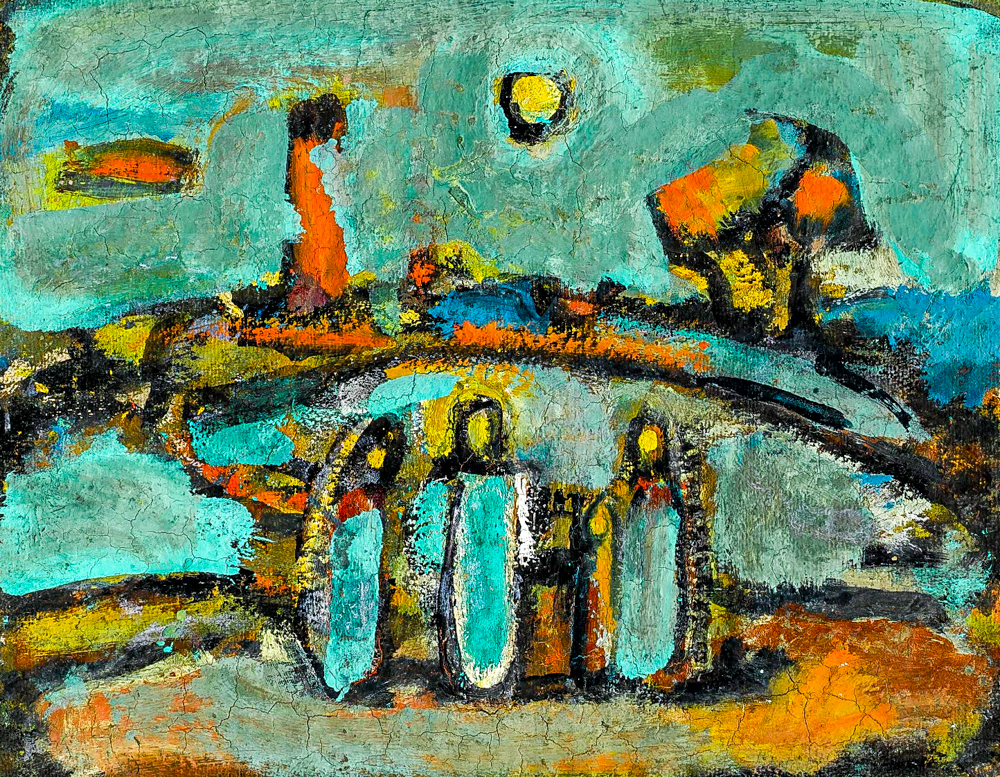
George Rouault's "Landscape of the Bible"

Henry Charles Munger's' The Rock '

Raul Dufei's "The Nearby Hills"
Painters near Russia are no longer satisfied with following the art of Italian and French academies. Alexei Kondratyevich Savrasov (Belarus, 1830-1897), the founder of the Russian landscape painting school, explored deeper meanings through nature. He extracted the most spiritually charged natural "emotions" from the desolate land of Russia, earning him the title of a landscape painter rich in national sentiment. In 1863, the Royal Academy of Fine Arts in Peterborough held a painting competition titled "Valhalla Palace". Fourteen graduates of the academy believed that the topic was too unrealistic, and the academy immediately dismissed them. In 1870, these painters formed the "Russian Artists Tour Exhibition Association", mainly depicting the natural scenery of Russia and the daily lives of the middle class and farmers. In 1871, members of the "Russian touring painting school" held their first art exhibition in St. Petersburg. Vasily Grigorievich Perov (Russia, 1834-1882)'s works reflect the strong voice of the people and his sympathy for the working masses, and his creations have had a significant impact on the development of the Moscow School of Painting. Ivan Nikolaevich Kramskoy (Russia, 1837-1887) placed great emphasis on the artistic form of expressing national style, originality, and profound ideas, which had a great influence on the Russian art world and young painters. Ilya Efimovich Repin (Russia, 1844-1930) created a large number of historical paintings, genre paintings, and portrait paintings, which depicted the hardships and desires of people's lives. Ivan I Shishkin (Russia, 1832-1898), known as the "forest singer of Russia," depicted the mystery and grandeur of the northern forests of Russia, and felt the personality of the Russian nation from his paintings. He is regarded as a milestone in the development of Russian landscape painting. Vasily Ivanovich Surikov (Russia, 1848-1916) always tried to depict the unique scenery of Russia in his paintings, expressing his love for the nature of his homeland. The works of Isaac Iliich Levitan (1860-1900, Russia) are highly poetic and deeply and authentically depict the natural characteristics and beauty of Russia. Valentin Serov (Russia, 1865-1911)'s sincerity and persistence in art, as well as his love for his homeland and nature, ultimately formed his realistic painting style.

Alexei Kondratvich Safrasov's "A Day in Spring"
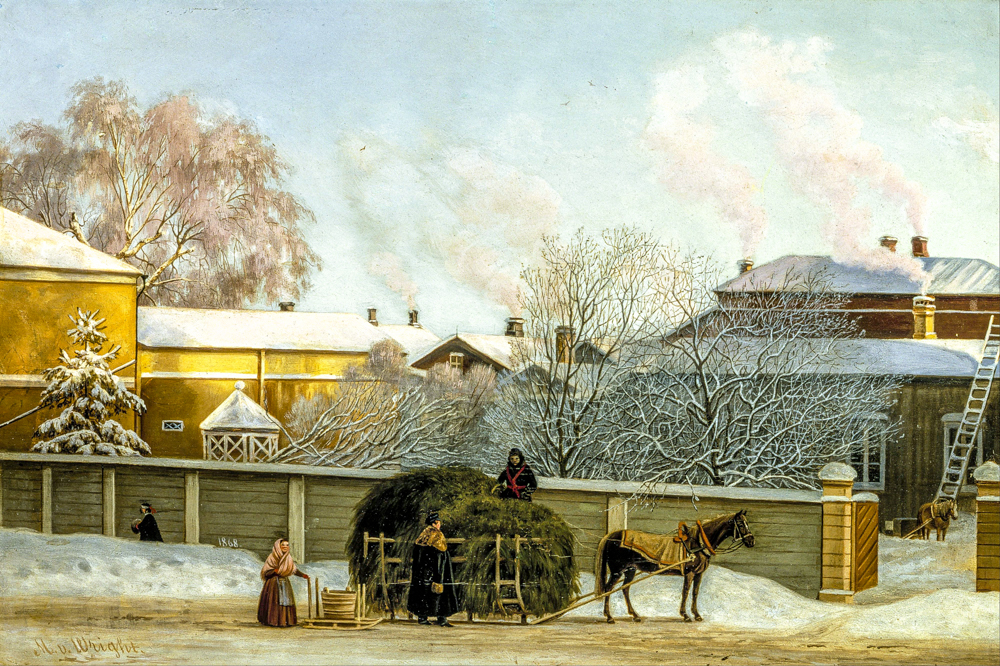

Vasily Grigorievich Pirov's "Annanakatu on a Cold Winter Morning"

Ivan Nikolaevich Kramsky's "The Mermaid"
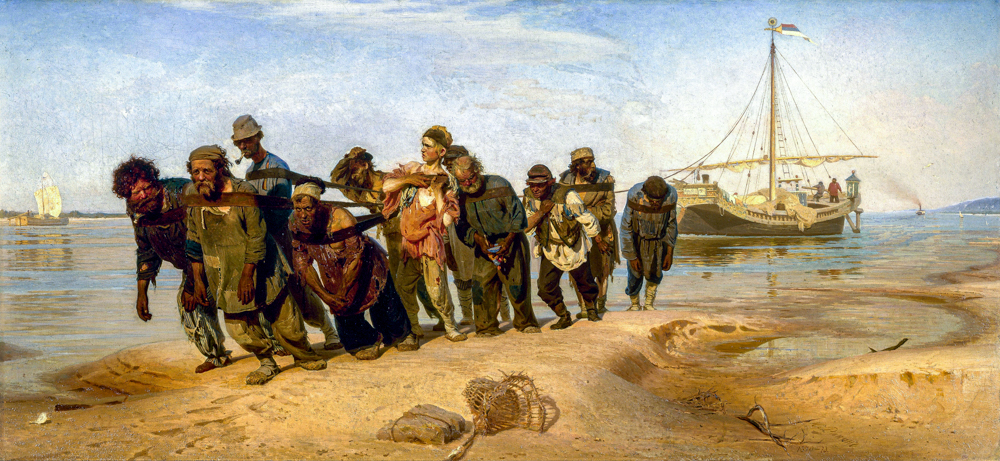

Ilya Yefimovich Repin's "The Fives on the Volga River"
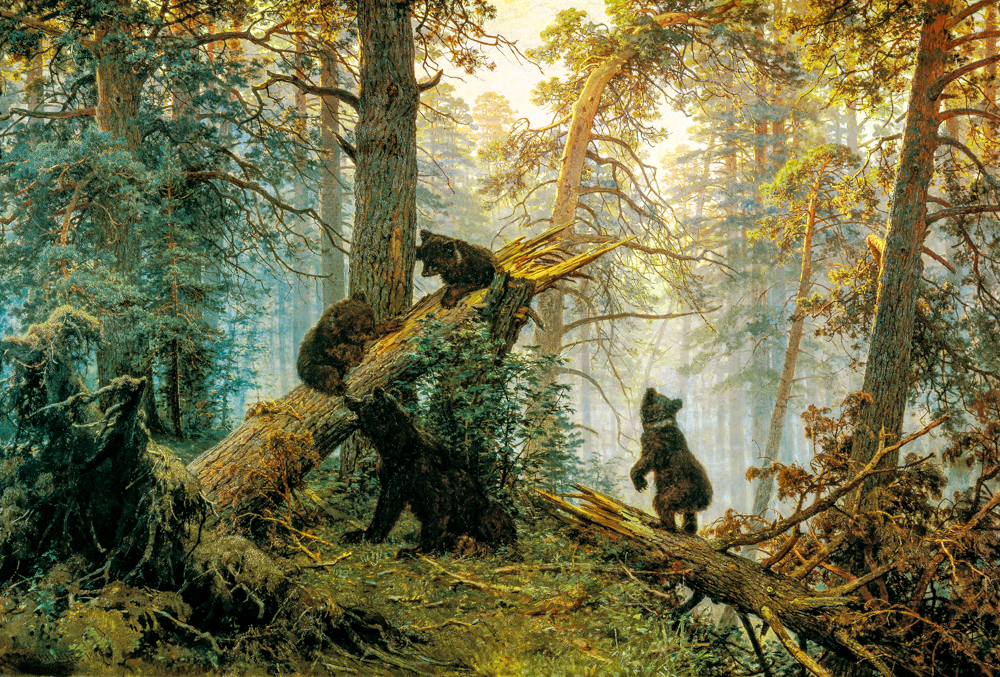

Ivan Ivanovich Hirschkin's' Morning in the Pine Forest '
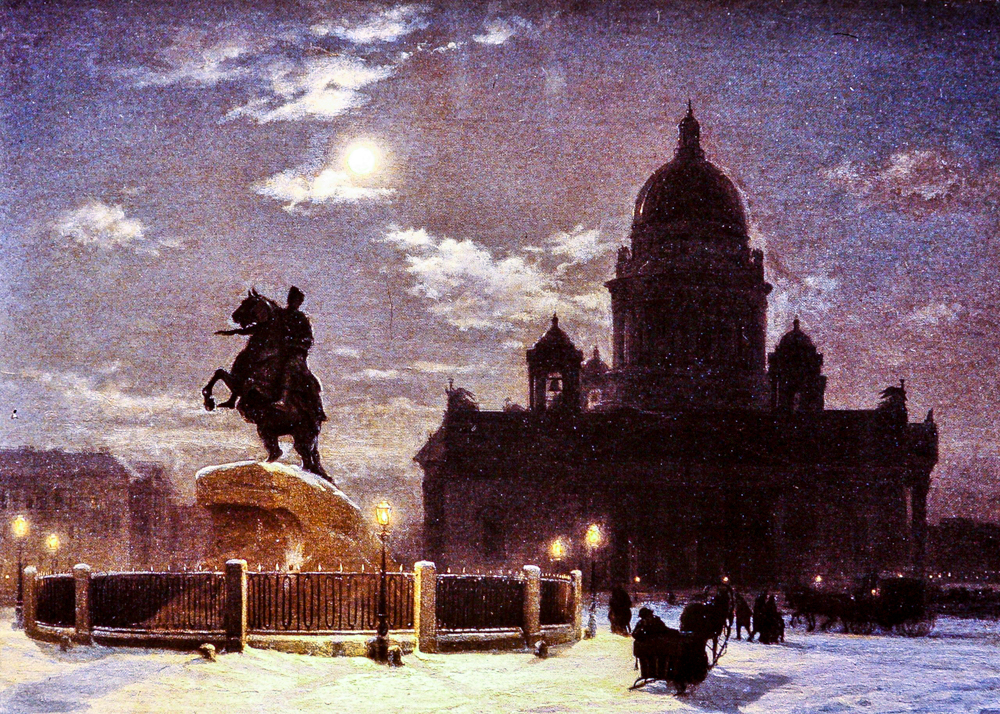

Vasily Ivanovich Surikov's' Bronze Knight '
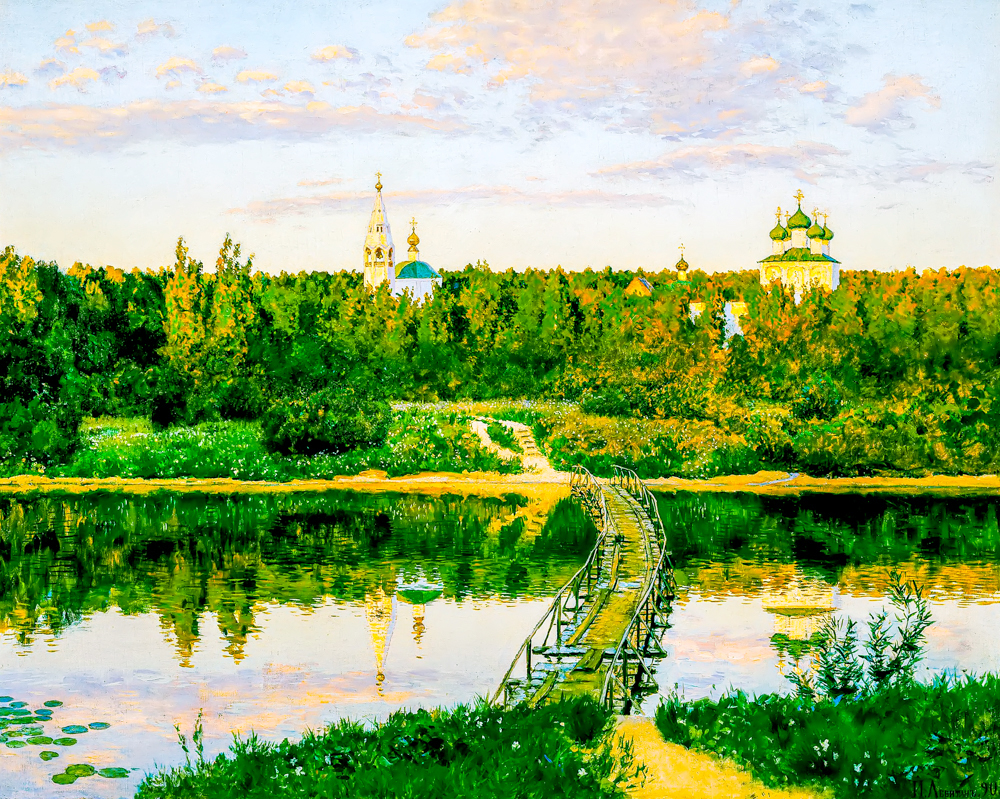

Isaac Ilyich Leviathan's "The Quiet Monastery"

Valentin Shilov's "October"
Painters from different countries resided in Paris and formed their own artistic language through continuous realistic creation, known as the "Paris School of Painting". Amedeo Modigliani (Italy, 1884-1920) used beautiful and refined lines to outline the contours of objects, and then applied exaggerated and refined rich colors to create a rhythmic and beautiful rhythm in the picture. Maurice Utrillo (France, 1883-1955) is known as the "poet of nature" for his delicate brushstrokes and precise colors in depicting natural landscapes, particularly adept at capturing changes in light and atmosphere. Chaim Soutine (France, 1894-1943) is known to the world for his heavy brushstrokes, rich colors, and exaggerated shapes. Through abstract and deformed painting language, he expresses his negative attitude towards the entire society.

Amedeo Modigliani's "Scenery of Cagne"
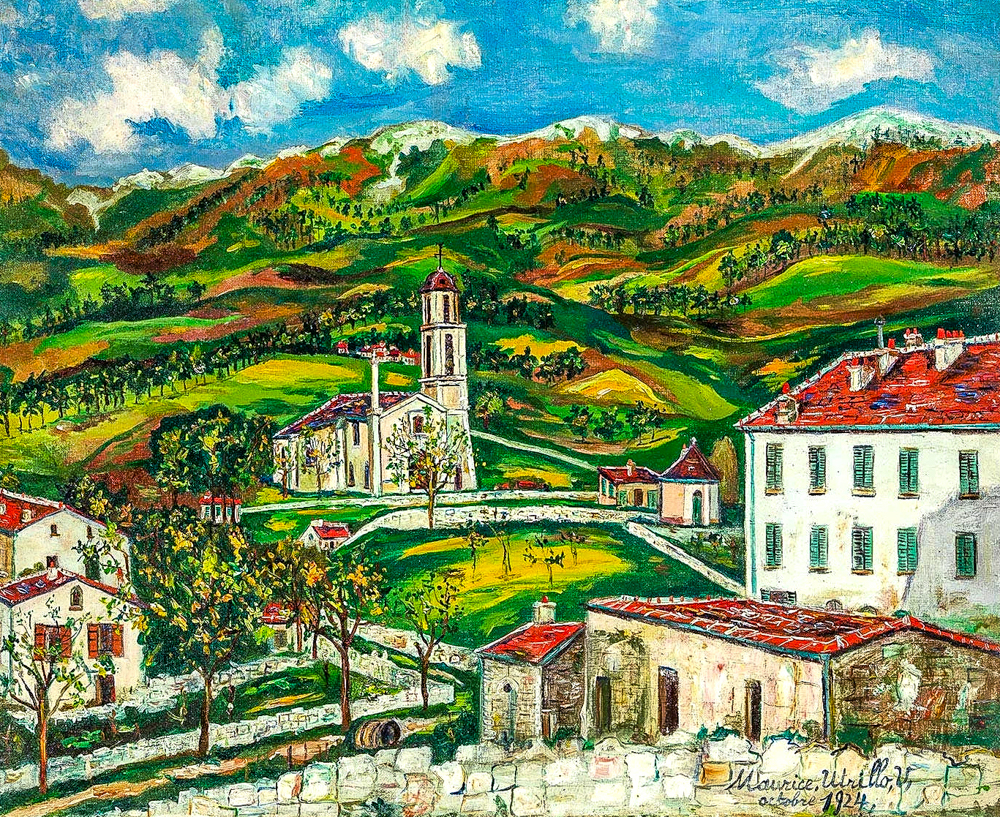

Maurice Utrillo's' Scenery of Corsica '

Chaim Sudin's "The House with a Sharp Roof"
Wassily Kandinsky (Russia, 1866-1944) was knowledgeable and proficient in music, and had a systematic study of Western modern philosophy. He summarized a complete theory of abstract art, which includes two aspects: firstly, art is not an objective imitation of nature, but an expression of inner spirit; Secondly, artistic expression should be abstract, and concrete images hinder the transmission of spirit. Piet Cornelies Mondrian (Netherlands, 1872-1944) painted realistic figures and landscapes in his early years, gradually simplifying the form of trees into purely abstract compositions of horizontal and vertical lines. Through introspection and insight, he created a universal aesthetic of order and balance. Kazimir Severinovich Malevich (Russia, 1878-1935) established the unique artistic style of solo dance through simple abstract geometric forms and later concrete geometric forms in black and white or bright colors. He once said, "Imitative art must be destroyed.

Vasily Kandinsky's "City Scenery"

Pete Cornelis Mondrian's Broadway Jazz

Kasimir Severovich Malevich's' Morning in the Village After a Snowstorm '
Since the 20th century, more categories of landscape painters have emerged. Edward Hopper (1882-1967) was a leader in modern realism painting in the United States. He had exquisite skills in handling concreteness and abstraction, color and texture, form and light and shadow. He used simple geometric forms to compose and depicted dramatic light and shadow through the light and shadow of flat stacked blocks.
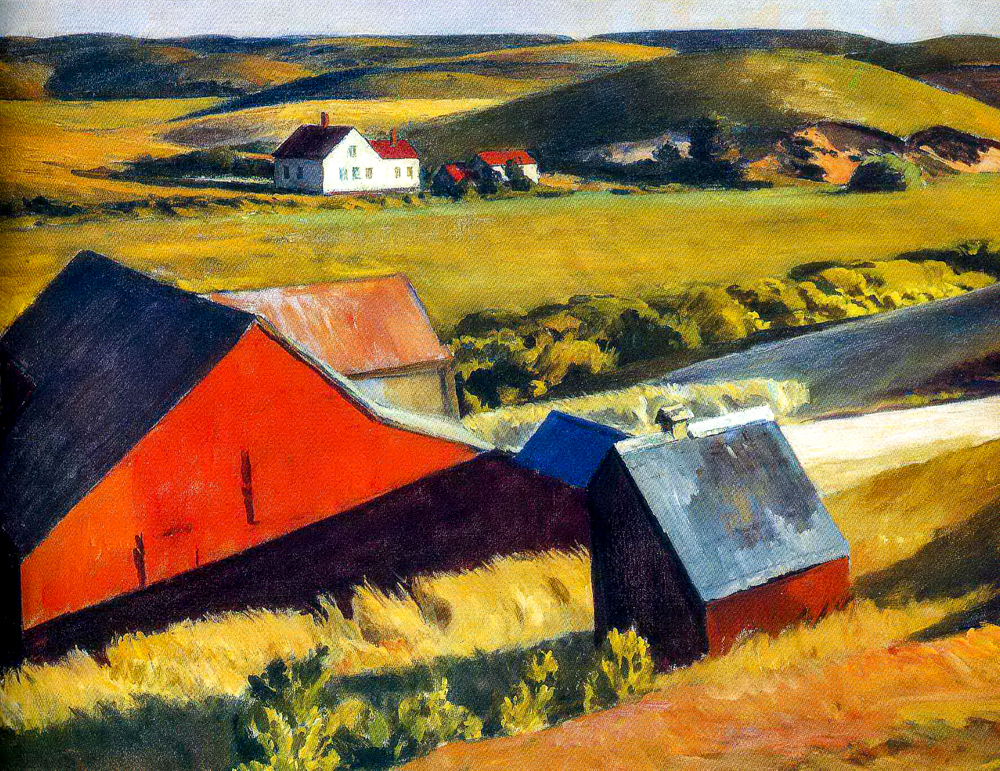

Edward Hopper's "Cobb's Barn and the House in the Distance"
Giorgio Morandi (Italy, 1890-1964) constantly modified the structure, softened colors, filtered out details, and created an almost abstract picture, making his works completely transcend "still life" landscapes and have a purely spiritual monument like meaning. Baltis: "Morandi is undoubtedly the closest European painter to Chinese painting. He saves ink to the extreme, and his paintings have a unique realm
George Morandi's' Snowscapes'
Kaii Higashiyama (1908-1999) captured the beauty of Japanese style with a Western realistic perspective and was adept at depicting pure nature that had not been polluted by modern civilization. His works enhance the sense of space while maintaining flatness, with a decorative and picturesque style that is elegant and understated, full of poetic philosophy and a hint of sadness.
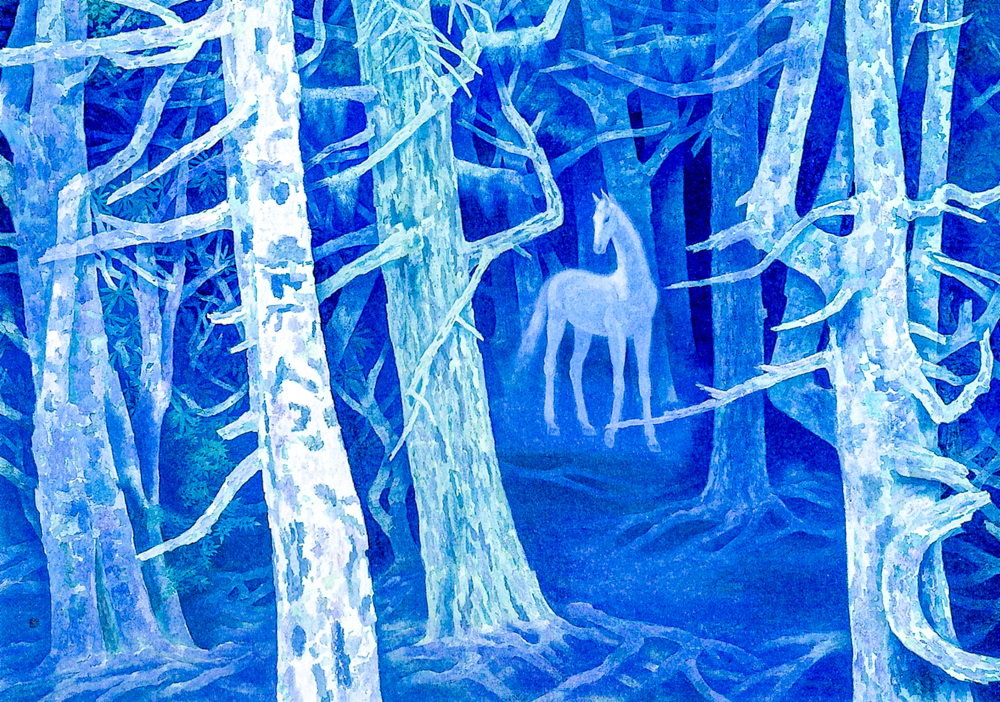

Dongshan Kuiyi's "White Horse Forest"
Balthasar Klossowski de Rola (1908-2001, France) did not enter the Academy of Fine Arts to study painting, but instead copied the paintings of ancient masters at the Louvre. It advocates a retro spirit and highly admires the skills of painters such as Francisco Guardi, Tommaso di Giovanni di Simone Guidi (known as the "realist pioneers"), Giotto di Bondona (known as the "father of European painting"), Nicolas Pusan, and others, pushing figurative painting to a new height.
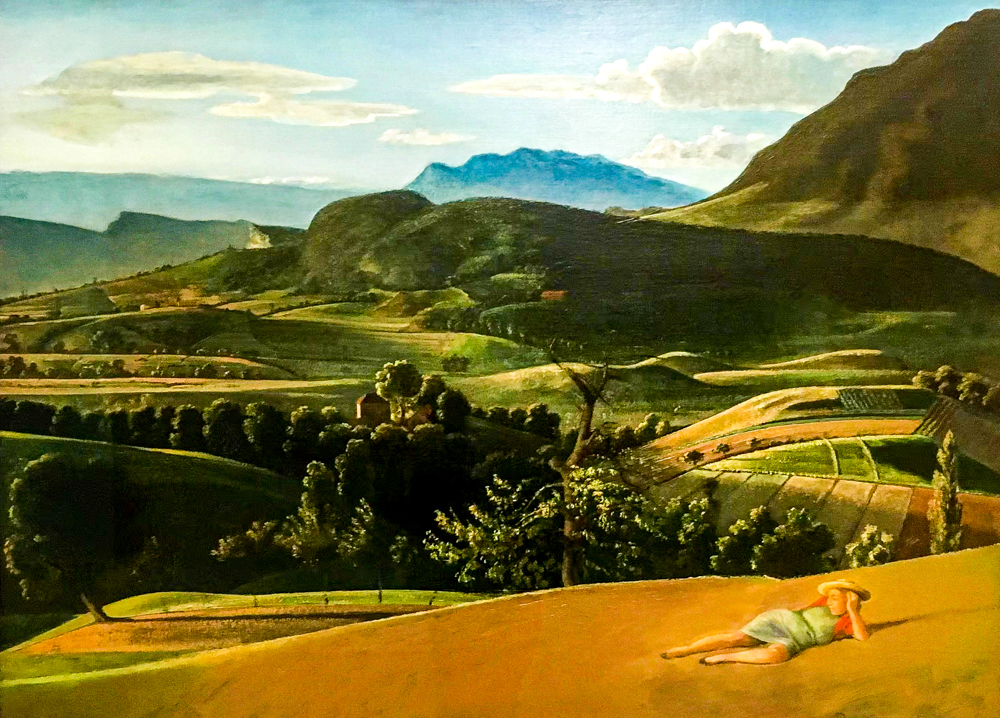

Balthazar Klosovsky de Lora's "Provence Scenery"
Andrew Wyeth (1917-2009), as a neorealist painter, depicted the natural environment around his life through watercolor and tempera paintings. He used "extracted abstractions" as painting elements, delving deep into the surface of nature and incorporating personal subjective ideals and desires into his works, forming thought-provoking art with profound connotations.

Andrew Wise's "Hunter"
Lucian Freud (1922-2011) was an expressionist painter who used heavy brushstrokes to create color shapes. His mastery of color was no longer limited to shaping the image of characters, but rather transformed color into a meaningful life. In the later stage, his focus gradually shifted from the meaning generated by gray and physical changes to the emphasis on the language of form itself.
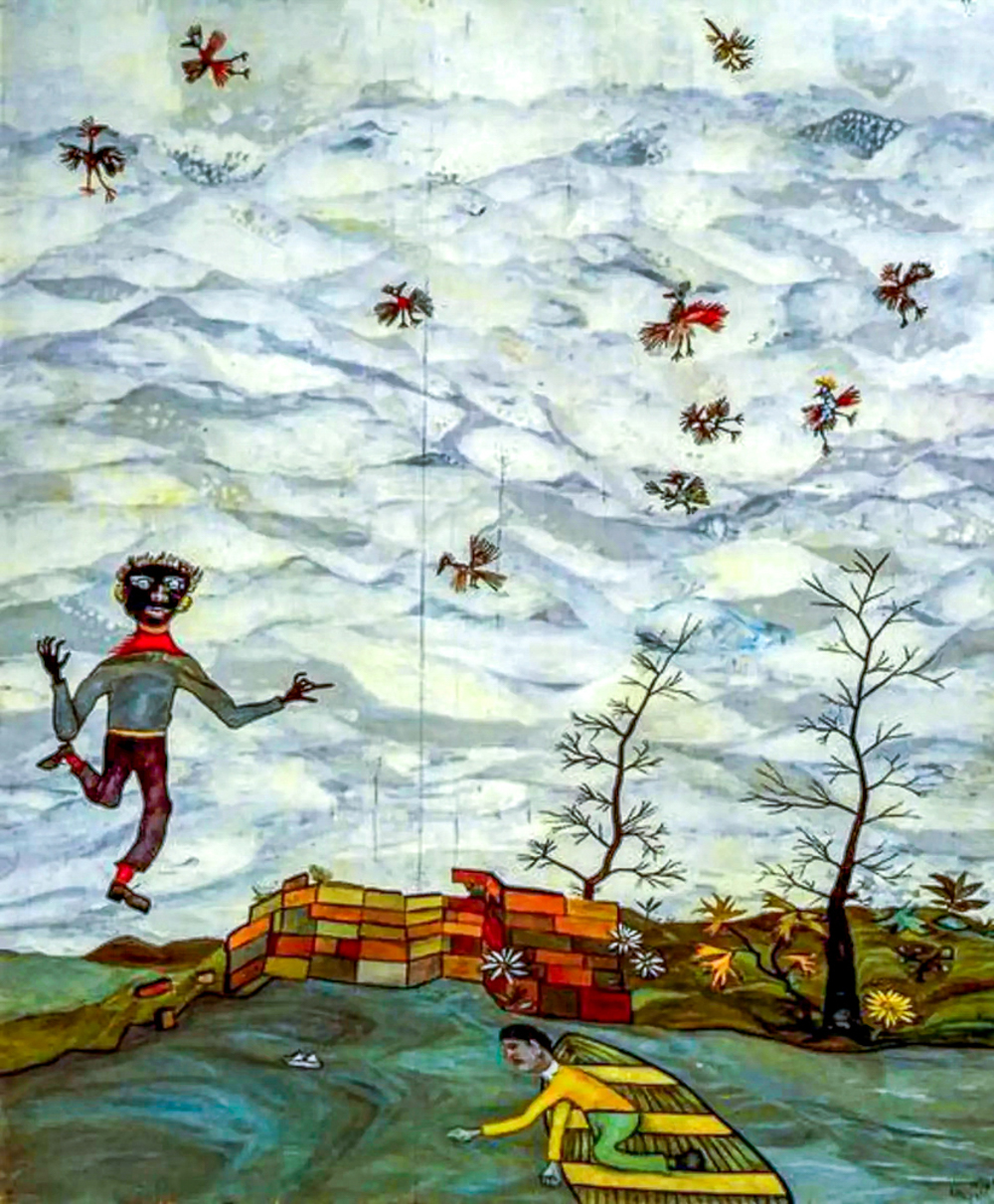

Lucien Freud's "Aerial View"
Frank Auerbach (born 1931 in the United Kingdom) is known for his precise and powerful brushwork. The images in his works often take months, or even years, to come to life, and the meaning of the concrete images naturally appears, thus avoiding "possible interpretations". He once said, "Art is about forgetting oneself and acting on instinct

Frank Auerbach's' Moonington Crescent '
Antonio Lopez Garcia (Spain, 1936-) had expressionist style in his works around 1955, magical realism style in his works from 1956 to 1965, and photographic realism style in his works after 1965. It abandons the relatively harmonious single color in Western classical painting, as well as the strong contrast and composition of pure colors commonly found in modern and contemporary painting. It establishes its own unique color system and uses traditional realistic painting language to explore the beauty of common objects, making them have a strong sense of presence, surpassing the limitations of specific scenes, and thus entering the depths of the viewer's soul.
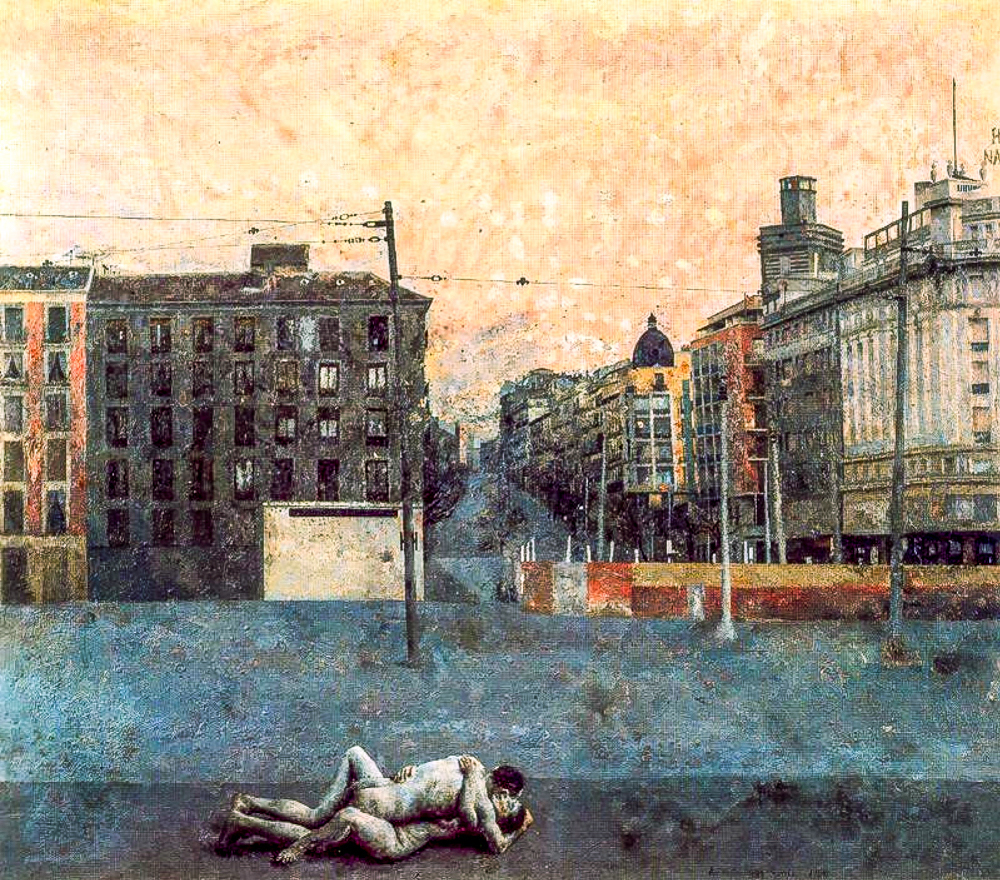

Antonio Lopez Garcia's' Atocha '
David Hockney (UK, 1937-) created photo collages in his early years, using Polaroids to collage photos taken from different angles into an image, which he regarded as a "new way of viewing the world". He is constantly discovering that whether it is the way of viewing or the way of creating, he once said, "Teachers can only impart skills, not poetry
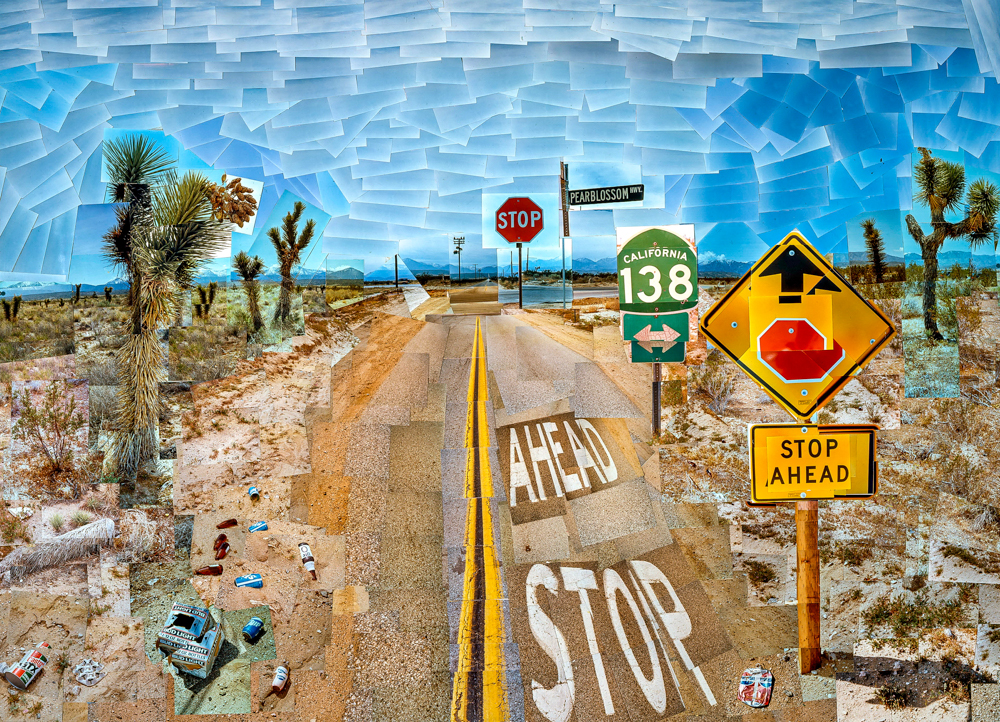

David Hockney's' The Road of Pear Blossoms'
© CopyRight 2023 Yu Yue Photocopying Shanghai ICP No. 2023013283




